Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| PROC CAPABILITY and General Statements |
The CAPABILITY procedure provides several methods for computing robust estimates of location and scale, which are insensitive to outliers in the data.


The Winsorized mean is the mean computed after replacing the k smallest observations with the (k+1)st smallest observation, and the k largest observations with the (k+1)st largest observation.
For data from a symmetric distribution, the Winsorized mean is an unbiased estimate of the population mean. However, the Winsorized mean does not have a normal distribution even if the data are normally distributed.
The Winsorized sum of squared deviations is defined as

A Winsorized t test is given by
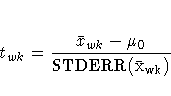

A ![]() % Winsorized confidence interval for the
mean has upper and lower limits
% Winsorized confidence interval for the
mean has upper and lower limits
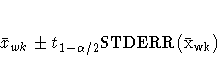


The trimmed mean is the mean computed after the k smallest observations and the k largest observations in the sample are deleted.
For data from a symmetric distribution, the trimmed mean is an unbiased estimate of the population mean. However, the trimmed mean does not have a normal distribution even if the data are normally distributed.
A robust estimate of the variance of the trimmed mean ttk can be obtained from the Winsorized sum of squared deviations; refer to Tukey and McLaughlin (1963). the corresponding trimmed t test is given by


When the data are from a symmetric distribution, the distribution of ttk is approximated by a Student's t distribution with n-2k-1 degrees of freedom. Refer to Tukey and McLaughlin (1963) and Dixon and Tukey (1968).
A ![]() % trimmed confidence interval for the
mean has upper and lower limits
% trimmed confidence interval for the
mean has upper and lower limits

The interquartile range (IQR) is simply the difference
between the upper and lower quartiles.
For a normal population, ![]() can be estimated as IQR/1.34898.
can be estimated as IQR/1.34898.
Gini's mean difference is computed as
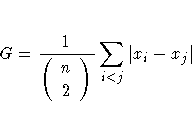
A very robust scale estimator is the MAD, the median absolute deviation from the median (Hampel, 1974), which is computed as

The MAD has low efficiency for normal distributions, and it may not always be appropriate for symmetric distributions. Rousseeuw and Croux (1993) proposed two statistics as alternatives to the MAD. The first is

The second statistic is


 distances between the data points.
The bias-corrected statistic
cqnQn
is used to estimate
distances between the data points.
The bias-corrected statistic
cqnQn
is used to estimate
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.