Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| Functions |
where
| n | is the sample size. |
| x | is the point of interest; that is, the PROBMED function calculates the probability that the median is less than or equal to x. |
Let n represent the sample size and X(i) represent the ith order statistic. Then, when n is odd, the function calculates
![\Pr[X_{((n+1)/2)}\leq x] = I_{\Phi(x)} ( \frac{n+1}2,
\frac{n+1}2 )](images/ap3eq63.gif)
where
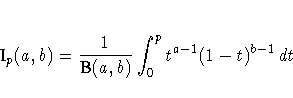
![{Pr} [ \frac{ X_{(n/2)} + X_{((n/2)+1)} }
2 \leq x ]
=](images/ap3eq66.gif)
![{} \frac 2
{ B(\frac{n}2,\frac{n}2) }
{\displaystyle \int_{-\infty}^x}
\{ [1-\Phi(u)]^{n/2}-[1-\Phi(2x-u)]^{n/2} \}
[\Phi(u)]^{(n/2)-1} \, \phi(u) \, du](images/ap3eq67.gif)
where B![]() and
and ![]() and
and
![]() are the standard normal cumulative
distribution function and density function, respectively.
are the standard normal cumulative
distribution function and density function, respectively.
For more information, refer to David (1981).
data;
b=probmed(5,-0.1);
put b;
run;
result in a value of 0.4256380897.
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.