Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The CLUSTER Procedure |
A dissimilarity measure d(x,y) is called an ultrametric if it satisfies the following conditions:
Any hierarchical clustering method induces a dissimilarity measure on the observations, say h(xi,xj). Let CM be the cluster with the fewest members that contains both xi and xj. Assume CM was formed by joining CK and CL. Then define h(xi,xj) = DKL.
If the fusion of CK and CL reduces the number of clusters from g to g - 1, then define D(g) = DKL. Johnson (1967) shows that if
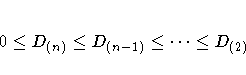
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.