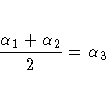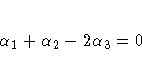CONTRAST Statement
- CONTRAST 'label' row-description <,... row-description><
/options >;
where a row-description is: effect values <,...effect values>
The CONTRAST statement provides a mechanism for obtaining customized
hypothesis tests. It is similar to the CONTRAST statement in
PROC GLM and PROC CATMOD, depending on the coding schemes used with any
classification variables involved.
The CONTRAST statement enables you to specify a matrix, L,
for testing the hypothesis  .You must be familiar with the details of the
model parameterization that PROC LOGISTIC uses
(for more information, see the PARAM= option in the section "CLASS Statement").
Optionally, the CONTRAST statement enables you to
estimate each row,
.You must be familiar with the details of the
model parameterization that PROC LOGISTIC uses
(for more information, see the PARAM= option in the section "CLASS Statement").
Optionally, the CONTRAST statement enables you to
estimate each row,  , of
, of
 and test the
hypothesis
and test the
hypothesis  .Computed statistics are based on the asymptotic chi-square
distribution of the Wald statistic.
.Computed statistics are based on the asymptotic chi-square
distribution of the Wald statistic.
There is no limit to the number of CONTRAST statements
that you can specify,
but they must appear after the MODEL statement.
The following parameters are specified in the CONTRAST statement:
- label
- identifies the contrast on the output.
A label is required for every contrast specified, and it
must be enclosed in
quotes. Labels can contain up to 256 characters.
- effect
- identifies an effect that appears in the MODEL statement.
The name INTERCEPT can be used as an effect when
one or more intercepts are included in the model.
You do not need to include all effects
that are included in the MODEL statement.
- values
- are constants that are elements of the
L matrix associated with the effect.
To correctly specify your contrast, it is crucial to know the
ordering of parameters within each effect and the variable levels
associated with any parameter. The "Class Level Information" table
shows the ordering of levels within variables. The E option,
described later in this section, enables you to verify the
proper correspondence of
values to parameters.
The rows of L are specified in order and
are separated by commas.
Multiple degree-of-freedom hypotheses can be tested by specifying
multiple row-descriptions.
For any of the full-rank parameterizations,
if an effect is not specified in the CONTRAST statement,
all of its coefficients in the L matrix are set to 0.
If too many values are specified for
an effect, the extra ones are ignored.
If too few values are specified,
the remaining ones are set to 0.
When you use effect coding
(by default or by specifying PARAM=EFFECT in the CLASS statement),
all parameters are directly estimable
(involve no other parameters).
For example, suppose an effect coded CLASS variable A has four
levels. Then there are three parameters ( ) representing the first three levels, and the fourth
parameter is represented by
) representing the first three levels, and the fourth
parameter is represented by
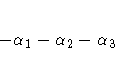
To test the first versus the fourth level of A,
you would test
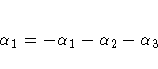
or, equivalently,
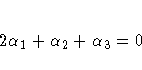
which, in the form  , is
, is
![[ 2 & 1 & 1 ] [
\alpha_1 \ \alpha_2 \ \alpha_3 ] = 0](images/lgseq23.gif)
Therefore, you would use the following CONTRAST statement:
contrast '1 vs. 4' A 2 1 1;
To contrast the third level with the average
of the first two levels, you would test
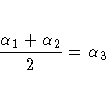
or, equivalently,
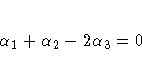
Therefore, you would use the following CONTRAST statement:
contrast '1&2 vs. 3' A 1 1 -2;
Other CONTRAST statements are constructed similarly. For
example,
contrast '1 vs. 2 ' A 1 -1 0;
contrast '1&2 vs. 4 ' A 3 3 2;
contrast '1&2 vs. 3&4' A 2 2 0;
contrast 'Main Effect' A 1 0 0,
A 0 1 0,
A 0 0 1;
When you use the less than full-rank
parameterization (by specifying PARAM=GLM in the CLASS statement),
each row is checked for estimability.
If PROC LOGISTIC finds a contrast to be nonestimable, it
displays missing values in corresponding rows in the results.
PROC LOGISTIC handles missing level combinations of classification
variables in the same manner as PROC GLM.
Parameters corresponding to missing level
combinations are not included in the model.
This convention can affect the way in which you specify
the L matrix in your CONTRAST statement.
If the elements of L are not specified for an effect that
contains a specified effect, then the elements of the specified
effect are distributed over the levels of the higher-order effect
just as the GLM procedure does for its CONTRAST and ESTIMATE statements.
For example, suppose that the model contains
effects A and B and their interaction A*B.
If you specify a CONTRAST statement involving A
alone, the L matrix contains nonzero
terms for both A and A*B, since A*B contains A.
The degrees of freedom is the number of linearly
independent constraints implied by the CONTRAST
statement, that is, the rank of L.
You can specify the following options after a slash (/).
- ALPHA= value
-
specifies the significance level of the confidence interval for
each contrast when the ESTIMATE option is specified. The default is
ALPHA=.05, resulting in a 95% confidence interval for each contrast.
- E
-
requests that the L matrix be displayed.
- ESTIMATE=keyword
-
requests that each individual contrast
(that is, each row,
 , of
, of  )or exponentiated contrast (
)or exponentiated contrast ( )be estimated and tested. PROC LOGISTIC displays the point estimate,
its standard error, a Wald confidence interval and
a Wald chi-square test for each contrast.
The significance level of the confidence interval is controlled by
the ALPHA= option.
You can
estimate the contrast or the exponentiated contrast
(
)be estimated and tested. PROC LOGISTIC displays the point estimate,
its standard error, a Wald confidence interval and
a Wald chi-square test for each contrast.
The significance level of the confidence interval is controlled by
the ALPHA= option.
You can
estimate the contrast or the exponentiated contrast
( ), or both, by
specifying one of the following keywords:
), or both, by
specifying one of the following keywords:
- PARM
- specifies that the contrast itself be estimated
- EXP
- specifies that the exponentiated contrast be estimated
- BOTH
- specifies that both the contrast and the exponentiated
contrast be estimated
- SINGULAR = number
-
tunes the estimability check.
This option is ignored when the
full-rank parameterization is
used.
If v is a vector, define ABS(v) to be the absolute
value of the element of v with the largest absolute value.
Define C to be equal to ABS(K') if
ABS(K') is greater than 0; otherwise,
C equals 1 for a row K' in the contrast.
If ABS(K' - K'T)
is greater than C*number, then K
is declared nonestimable. The
T matrix is the Hermite form matrix
(X'X)-(X'X), and
(X'X)- represents a generalized
inverse of the matrix X'X.
The value for number must be between
0 and 1; the default value is 1E-4.
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.
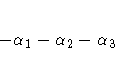
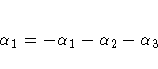
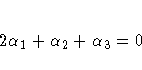
![[ 2 & 1 & 1 ] [
\alpha_1 \ \alpha_2 \ \alpha_3 ] = 0](images/lgseq23.gif)