Name:
Student Number
STAT 380
Final Examination
Richard Lockhart 7 December 2000
=1=Instructions:
This is an open book exam. You may use notes,
books and a calculator. The exam is out of 50.
I will be marking for clarity of
explanation as well as correctness.
- 1.
- A commuter has two possible routes to work, A and B. There
is construction activity on route A about 1 day in 20, and on route
B about 1 day in 10. If the commuter takes route A and
finds construction she switches to route B for the next day otherwise she uses
A again. If the commuter takes route B and finds construction she switches
to route A for the next day; otherwise she uses B again.
In the long run on what fraction of days does she commute via route
A and on what fraction of her trips does she find construction?
Your answer must set down clearly what assumptions you are making
to answer the question. Answers with inadequate explanations
will get low marks. [9 marks]
Extra space for Q1
- 2.
- Each day a random number of newspapers arrive at my house. The
probability that k papers arrive is
 At the end of the day I may or may not decide to throw out some
of the papers that have accumulated. Given that
there are m papers the probability that I throw j of them out is 1/(m+1)for
At the end of the day I may or may not decide to throw out some
of the papers that have accumulated. Given that
there are m papers the probability that I throw j of them out is 1/(m+1)for
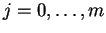 .
Let Xn be the number of papers left at the end of day n
(after I do the throwing out).
.
Let Xn be the number of papers left at the end of day n
(after I do the throwing out).
- (a)
- What must you assume in order to have Xn be a Markov chain?
[2 marks]
- (b)
- Suppose U is a random variable with
Show that
 .
[2 marks]
.
[2 marks]
- (c)
- Let
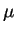 be the expected number of papers delivered to my house on
a given day.
Show that [3 marks]
be the expected number of papers delivered to my house on
a given day.
Show that [3 marks]
- (d)
- Let m be the long run expected number of papers I have at the
end of a day. That is
Show that  .
[3 marks]
.
[3 marks]
- 3.
- Suppose a Markov Chain has state space
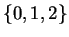 and
transition matrix
and
transition matrix
and initial distribution
(1/5,2/5,2/5).
- (a)
- Find
P(X2=0,X1=0,X0=0) [1 mark]
- (b)
- Find
P(X1=0|X2=0,X0=0) [2 marks]
- (c)
- Find the stationary initial distribution for this chain.
[2 marks]
- (d)
- Starting from state 0 how many steps do you expect to need to
get to state 2. [3 marks]
- 4.
- Cases of a rare medical condition arrive at a hospital
at the rate of 5 per week. Assuming that these arrivals form
a Poisson process and that last week there were actually 6 cases
what is the conditional probability that all 6 occurred on
Saturday or Sunday? [5 marks]
- 5.
- A container contains n particles; some are black
and the rest are white. Assume that collisions
between particles in the container occur at the times of a
Poisson process with rate
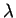 .
When a collision occurs
it is equally likely to be between any of the n(n-1)/2 pairs
of particles. When two black particles
collide there is a chance p that (precisely) one will turn white
(instantaneously); otherwise they both stay black.
When two white particles collide there is
a chance q that (precisely) one will turn black (instantaneously); otherwise
they both stay white. When two
opposite colour particles collide there is a chance r/2 that
they both become white and a chance r/2 that they both become
black.
.
When a collision occurs
it is equally likely to be between any of the n(n-1)/2 pairs
of particles. When two black particles
collide there is a chance p that (precisely) one will turn white
(instantaneously); otherwise they both stay black.
When two white particles collide there is
a chance q that (precisely) one will turn black (instantaneously); otherwise
they both stay white. When two
opposite colour particles collide there is a chance r/2 that
they both become white and a chance r/2 that they both become
black.
- (a)
- Describe an appropriate Markov Chain to analyze this system. Give
the transition matrix for the skeleton chain, the instantaneous transition
rates and the mean holding times in each state. [5 marks]
- (b)
- For n=3 what fraction of the time are all three balls
the same colour? [3 marks]
- 6.
- Suppose
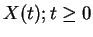 is a standard Brownian motion. Fix
0 < a < b.
is a standard Brownian motion. Fix
0 < a < b.
- (a)
- Show that [3 marks]
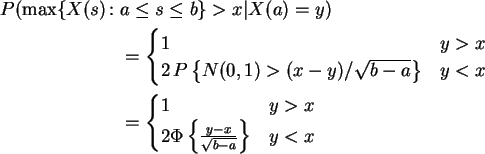
where
- (b)
- Use the formula in (a) to compute [3 marks]
A correct answer will involve an integral with the function  in it; DO NOT try to do the integral.
in it; DO NOT try to do the integral.
- 7.
- Suppose
 is a homogeneous Poisson Process
with rate
is a homogeneous Poisson Process
with rate 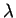 .
Find a function w(t) such that
.
Find a function w(t) such that
is a martingale (and prove that the w you have found works).
[4 marks]
Richard Lockhart
2002-04-10
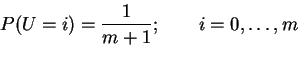
 .
[2 marks]
.
[2 marks]
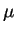 be the expected number of papers delivered to my house on
a given day.
Show that [3 marks]
be the expected number of papers delivered to my house on
a given day.
Show that [3 marks]
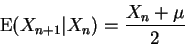
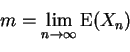
 .
[3 marks]
.
[3 marks]
![\begin{displaymath}\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 1/3 & 2/3 & 0 \\ 1/6 & 1/2 & 1/3 \\ 0 & 1/4 & 3/4
\end{array}\right]
\end{displaymath}](img10.gif)
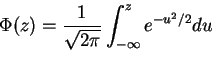
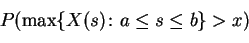
 in it; DO NOT try to do the integral.
in it; DO NOT try to do the integral.