Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| SAS Macros and Functions |
Assume that the transformed series Yt is a stationary pth order autoregressive process generated by independent normally distributed innovations.


Given these assumptions, the log likelihood function of the transformed data Yt is
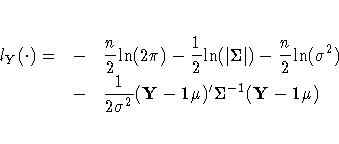
In this equation, n is the number of observations, ![]() is the mean of
Yt, 1 is the n-dimensional column vector of 1s,
is the mean of
Yt, 1 is the n-dimensional column vector of 1s,
![]() is the innovation variance,
Y = (Y1, ... ,Yn)', and
is the innovation variance,
Y = (Y1, ... ,Yn)', and ![]() is the covariance matrix of Y.
is the covariance matrix of Y.
The log likelihood function of the original data X1, ... , Xn is
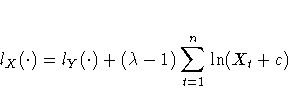
where c is the value of the CONST= option.
For each value of ![]() ,the maximum log likelihood of the original data is obtained from
the maximum log likelihood of the transformed data
given the maximum likelihood estimate of the autoregressive model.
,the maximum log likelihood of the original data is obtained from
the maximum log likelihood of the transformed data
given the maximum likelihood estimate of the autoregressive model.
The maximum log likelihood values are used to compute
the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)
and Schwarz's Bayesian Criterion (SBC) for each ![]() value.
The residual mean square error based on the maximum likelihood estimator
is also produced.
To compute the mean square error,
the predicted values from the model are re-transformed to
the original scale
(Pankratz 1983, pp. 256-258, and Taylor 1986).
value.
The residual mean square error based on the maximum likelihood estimator
is also produced.
To compute the mean square error,
the predicted values from the model are re-transformed to
the original scale
(Pankratz 1983, pp. 256-258, and Taylor 1986).
After differencing as specified by the DIF= option, the process is assumed to be a stationary autoregressive process. You can check for stationarity of the series with the %DFTEST macro. If the process is not stationary, differencing with the DIF= option is recommended. For a process with moving average terms, a large value for the AR= option may be appropriate.
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.