COVLAG Function
computes autocovariance estimates
for a vector time series
- COVLAG( x, k)
The inputs to the COVLAG function are as follows:
- x
- is an n ×nv matrix of time series
values; n is the number of observations, and
nv is the dimension of the random vector.
- k
- is a scalar, the absolute value of which
specifies the number of lags desired.
If k is positive, a mean correction is made.
If k is negative, no mean correction is made.
The COVLAG function computes a sequence
of lagged crossproduct matrices.
This function is useful for computing sample
autocovariance sequences for scalar or vector time series.
The value returned by the COVLAG
function is an nv ×(k*nv) matrix.
The ith nv ×nv block of the matrix is the sum

where xj is the jth row of x.
If k>0, then the ith nv ×nv block of the matrix is

where 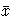 is a row vector of the column means of x.
For example, the statements
is a row vector of the column means of x.
For example, the statements
x={-9,-7,-5,-3,-1,1,3,5,7,9};
cov=covlag(x,4);
produce the matrix
COV 1 row 4 cols (numeric)
33 23.1 13.6 4.9
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.

