Hessian and CRP Jacobian Scaling
The rows and columns of the Hessian and crossproduct Jacobian matrix
can be scaled when using the trust-region, Newton-Raphson, Double Dogleg,
and Levenberg-Marquardt optimization techniques.
Each element Gi,j, i,j = 1, ... ,n, is divided by the
scaling factor di * dj, where the scaling vector
d = (d1, ... ,dn) is iteratively updated in a way
specified by the HESCAL=i option, as follows:
- i = 0
- : No scaling is done (equivalent to di=1).
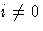
- : First iteration and each restart iteration sets:

- i = 1
- : refer to Mor
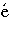 (1978):
(1978):

- i = 2
- : refer to Dennis, Gay, and Welsch (1981):

- i = 3
- : di is reset in each iteration:

where 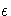 is the relative machine precision or, equivalently,
the largest double precision value that when added to 1 results in 1.
is the relative machine precision or, equivalently,
the largest double precision value that when added to 1 results in 1.
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.



