| The RELIABILITY Procedure |
Regression Model Observation-Wise Statistics
For regression models that are fit using the MODEL statement,
you can specify a variety of statistics to be
computed for each observation in the input data set. This
section describes the method of computation for each statistic. See
Table 30.21 and Table 30.22 for the syntax for requesting
these statistics.
Predicted Values
The linear predictor is

where xi is the vector of explanatory variables for the ith
observation.
Percentiles
An estimator of the p×100% percentile xp for the ith
observation for the extreme value, normal, and logistic
distributions is

where zp=G-1(p), G is the standardized CDF,
and 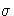 is the distribution scale parameter.
is the distribution scale parameter.
An estimator of the p×100% percentile tp for the ith
observation for the Weibull, lognormal, and log-logistic
distributions is
![\hat{t}_{i,p}=\exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ z_{p}\hat{\sigma}]](images/releq183.gif)
where G is the standardized CDF of the
extreme value, normal, or logistic distribution that corresponds to
the logarithm of the lifetime,
and 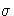 is the distribution scale parameter.
is the distribution scale parameter.
The percentile of the lognormal (base 10) distribution is
![\hat{t}_{i,p}=10^{[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ z_{p}\hat{\sigma}]}](images/releq184.gif)
where G is the CDF of the standard normal distribution.
An estimator of the p×100% percentile tp for the ith
observation for the generalized gamma
distribution is
![\hat{t}_{i,p} = \exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma}]](images/releq185.gif)
where

and 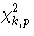 is the p×100% percentile of the
chi-squared distribution with k degrees of freedom.
is the p×100% percentile of the
chi-squared distribution with k degrees of freedom.
Standard Errors of Percentile Estimator
For the extreme value, normal, and logistic distributions, the
standard error of the estimator of the p×100%
percentile is computed as

where
![z=[ x_{i} \ z_{p}
]](images/releq189.gif)
and 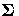 is the covariance matrix of
is the covariance matrix of 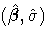 .
.For the Weibull, lognormal, and log-logistic distributions, the
standard error is computed as

where xi,p is the percentile computed from the extreme value,
normal, or logistic distribution that corresponds to the logarithm
of the lifetime.
The standard error for the lognormal (base 10) distribution is computed
as

The standard error for the generalized gamma distribution percentile is
computed as
![\sigma_{i,p} = \exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma}]\sqrt{z'{\Sigma z}}](images/releq194.gif)
where
![z=[ x_{i} \ w_{\lambda,p} \ \hat{\sigma}\frac{\partial w_{\lambda,p}}{\partial \lambda}
]](images/releq195.gif)
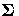 is the covariance matrix of
is the covariance matrix of
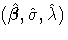 ,
, 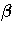 is the
vector of regression parameters,
is the
vector of regression parameters, 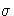 is the scale parameter, and
is the scale parameter, and
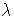 is the shape parameter.
is the shape parameter.
Confidence Limits for Percentiles
Two-sided approximate 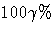 confidence limits for xi,p
for the extreme value, normal, and logistic distributions are
computed as
confidence limits for xi,p
for the extreme value, normal, and logistic distributions are
computed as

where 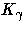 represents the
represents the 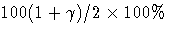 percentile of the standard normal distribution.
percentile of the standard normal distribution.
Limits for the Weibull, lognormal, and log-logistic percentiles are computed as

where xL and xU are computed from the corresponding distributions
for the logarithms of the lifetimes.
For the lognormal (base 10) distribution,

Limits for the generalized gamma distribution percentiles are computed as
![t_{L} = \exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma} - K_{\gamma}\sqrt{...
...x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma} + K_{\gamma}\sqrt{z'{\Sigma z}}]](images/releq200.gif)
Reliability Function
For the extreme value, normal, and logistic distributions, an estimate
of the reliability function evaluated at the response yi is
computed as

where G(x) is the standardized CDF of the distribution
from Table 30.47.
Estimates of the reliability function evaluated at the response
ti for the Weibull, lognormal,
log-logistic, and generalized gamma distributions are computed
as

where G(x) is the standardized CDF of the corresponding
extreme value, normal, logistic, or generalized log-gamma
distributions.
Residuals
The RELIABILITY procedure computes several different kinds of residuals.
In the following equations, yi represents the ith response value if the
extreme value, normal, or logistic distributions are specified.
If ti is the ith response and if the Weibull, lognormal, log-logistic,
or generalized gamma distributions are specified, then yi
represents the logarithm of the response yi = log(ti).
If the lognormal (base 10) distribution is specified, then
yi = log10(ti).
Raw Residuals
The raw residual is computed as

Standardized Residuals
The standardized residual is computed as

Adjusted Residuals
If an observation is right censored, then the standardized
residual for that observation is also right censored.
Adjusted residuals adjust censored
standardized residuals upward by adding a percentile of the
residual lifetime distribution, given that the standardized residual
exceeds the censoring
value. The default percentile is the median (50th percentile),
but you can, optionally, specify a 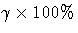 percentile using the
RESIDALPHA=
percentile using the
RESIDALPHA=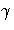 option in MODEL statement.
The
option in MODEL statement.
The 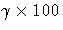 percentile residual life is computed as in
Joe and Proschan (1984).
The adjusted residual is computed as
percentile residual life is computed as in
Joe and Proschan (1984).
The adjusted residual is computed as
![r_{Ai}= \{ G^{-1}[1-(1-\gamma)S(u_{i})] & { for right-censored observations } \
u_{i} & { for uncensored observations }
.](images/releq205.gif)
where G is the standard CDF,
-
S(u)=1-G(u)
is the reliability
function, and

If the generalized gamma distribution is specified, the standardized
CDF and reliability functions include the estimated shape
parameter 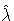 .
.Modified Cox-Snell Residuals
Let

The Cox-Snell residual is defined as
-
rCi = -log(R(yi))
where

is the reliability function.
The modified Cox-Snell residual is computed as in Collett (1994, p.152):

where 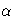 is an adjustment factor. If the fitted model is
correct, the Cox-Snell residual has approximately a standard exponential
distribution for uncensored observations.
If an observation is censored, the residual evaluated
at the censoring time is not as large as the residual evaluated
at the (unknown) failure time.
The adjustment factor
is an adjustment factor. If the fitted model is
correct, the Cox-Snell residual has approximately a standard exponential
distribution for uncensored observations.
If an observation is censored, the residual evaluated
at the censoring time is not as large as the residual evaluated
at the (unknown) failure time.
The adjustment factor 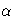 adjusts the
censored residuals upward to account for the censoring.
The default is
adjusts the
censored residuals upward to account for the censoring.
The default is 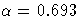 , the median of the
standard exponential distribution. You can, optionally, specify any
adjustment factor by using the MODEL
statement option RESIDADJ=
, the median of the
standard exponential distribution. You can, optionally, specify any
adjustment factor by using the MODEL
statement option RESIDADJ=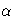 . Another commonly used value
is the mean of the standard exponential distribution,
. Another commonly used value
is the mean of the standard exponential distribution, 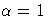 .
.Deviance Residuals
Deviance residuals are a zero-mean, symmetrized version of
modified Cox-Snell residuals.
Deviance residuals are computed as in Collett (1994, p.153):
![r_{Di}={\rm sgn}(\delta_{i}-r_{Ci})
\{-2[\delta_{i}-r_{Ci}+\delta_{i}\log(r_{Ci})]\}^{1/2}](images/releq212.gif)
where

Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.


![\hat{t}_{i,p}=\exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ z_{p}\hat{\sigma}]](images/releq183.gif)
![\hat{t}_{i,p}=10^{[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ z_{p}\hat{\sigma}]}](images/releq184.gif)
![\hat{t}_{i,p} = \exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma}]](images/releq185.gif)


![z=[ x_{i} \ z_{p}
]](images/releq189.gif)


![\sigma_{i,p} = \exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma}]\sqrt{z'{\Sigma z}}](images/releq194.gif)
![z=[ x_{i} \ w_{\lambda,p} \ \hat{\sigma}\frac{\partial w_{\lambda,p}}{\partial \lambda}
]](images/releq195.gif)



![t_{L} = \exp[{x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma} - K_{\gamma}\sqrt{...
...x_{i}}'\hat{{\beta}}+ w_{\lambda,p}\hat{\sigma} + K_{\gamma}\sqrt{z'{\Sigma z}}]](images/releq200.gif)




![r_{Ai}= \{ G^{-1}[1-(1-\gamma)S(u_{i})] & { for right-censored observations } \
u_{i} & { for uncensored observations }
.](images/releq205.gif)




![r_{Di}={\rm sgn}(\delta_{i}-r_{Ci})
\{-2[\delta_{i}-r_{Ci}+\delta_{i}\log(r_{Ci})]\}^{1/2}](images/releq212.gif)
