Survival Distribution Estimates for the Cox Model
Two estimators of the survivor function
are available: one is
the product-limit estimate and the other is based on
the empirical cumulative hazard function.
Product-Limit Estimates
Let Ci denote the
set of individuals censored in the half-open interval [ti , ti+1),
where t0=0 and 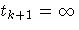 .Let
.Let 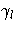 denote
the censoring times in
[ti , ti+1); l ranges over
Ci .
The likelihood function for all individuals is given by
denote
the censoring times in
[ti , ti+1); l ranges over
Ci .
The likelihood function for all individuals is given by
![{\cal L}=\prod_{i=0}^k
\{ \prod_{l \in {\cal D}_i}
( [S_{0}(t_{i})]^{ {\rm exp...
... )
\prod_{l \in {\cal C}_i} [S_{0}(\gamma_{l}+0)]^{{\rm exp}(z'_{l}{\beta})}
\}](images/phreq136.gif)
where D0 is empty.
The likelihood L is maximized by taking
S0(t)=S0(ti+0) for
 and allowing the
probability mass to fall only on the observed event times
t1, , tk.
By considering
a discrete model with hazard contribution
and allowing the
probability mass to fall only on the observed event times
t1, , tk.
By considering
a discrete model with hazard contribution
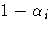 at ti, you take
at ti, you take
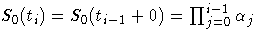 , where
, where
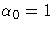 . Substitution into the likelihood function produces
. Substitution into the likelihood function produces
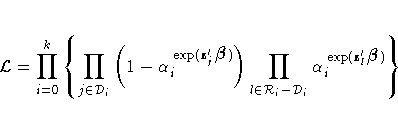
If you replace  with
with 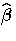 estimated from the partial
likelihood function and then
maximize with respect to
estimated from the partial
likelihood function and then
maximize with respect to 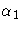 , ,
, ,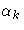 ,
the maximum likelihood estimate
,
the maximum likelihood estimate
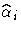 of
of 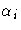 becomes a solution of
becomes a solution of
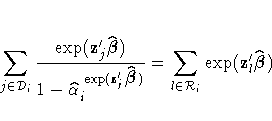
When only a single failure occurs at ti, 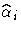 can be found explicitly. Otherwise,
an iterative solution is obtained by the Newton method.
can be found explicitly. Otherwise,
an iterative solution is obtained by the Newton method.
The estimated baseline cumulative hazard function is
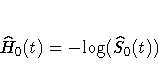
where 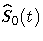 is the estimated baseline
survivor function given by
is the estimated baseline
survivor function given by
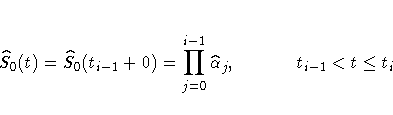
For details, refer to Kalbfleisch and Prentice (1980).
For a given realization of the
explanatory variables 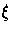 ,the product-limit estimate of the survival function at
,the product-limit estimate of the survival function at 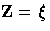 is
is
![\hat{S}(t,{\xi})= [\hat{S}_{0}(t)]^{\exp({\beta}'{\xi})}](images/phreq152.gif)
Empirical Cumulative Hazards Function Estimates
Let 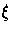 be a given realization of the
explanatory variables.
The empirical cumulative hazard function estimate
at
be a given realization of the
explanatory variables.
The empirical cumulative hazard function estimate
at 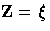 is
is
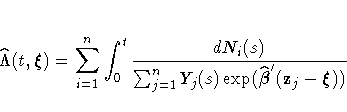
The variance estimator of 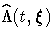 is given by
the following (Tsiatis 1981):
is given by
the following (Tsiatis 1981):
![& &\hat{var}\{n^{\frac{1}2}(\hat{\Lambda}(t,{\xi}) -
\Lambda(t,{\xi}))\} \ & = ...
...i}))]^2} + \biggr.
\biggl. H'(t,{\xi})\hat{V}(\hat{{\beta}})H(t,{\xi}) \biggr\}](images/phreq155.gif)
where 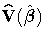 is the estimated covariance matrix of
is the estimated covariance matrix of 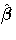 and
and
![H(t,{\xi}) = \sum_{i=1}^n\int_{0}^t
\frac{\sum_{l=1}^n Y_{l}(s)(Z_{l}-{\xi})\ex...
...{\xi}))}
{[\sum_{j=1}^n Y_{j}(s)\exp(\hat{{\beta}}'(z_{j} - {\xi}))]^2} dN_i(s)](images/phreq157.gif)
The empirical cumulative hazard function (CH) estimate of the
survivor function for 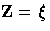 is
is
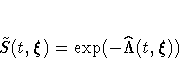
Confidence Intervals for the Survivor Function
Let 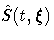 and
and  correspond to the product-limit (PL) and
empirical cumulative hazard function (CH) estimates of the survivor function
for
correspond to the product-limit (PL) and
empirical cumulative hazard function (CH) estimates of the survivor function
for 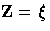 , respectively.
Both the standard error of log(
, respectively.
Both the standard error of log(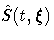 ) and the standard error of
log(
) and the standard error of
log( ) are approximated by
) are approximated by 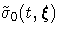 , which is the
square root of the variance estimate of
, which is the
square root of the variance estimate of
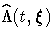 ; refer to Kalbfleish and
Prentice (1980, p. 116). By the
delta method, the standard errors of
; refer to Kalbfleish and
Prentice (1980, p. 116). By the
delta method, the standard errors of 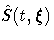 and
and  are given by
are given by
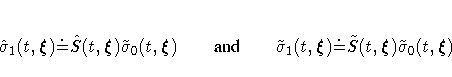
respectively. The standard errors of log[-log(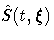 )] and
log[-log(
)] and
log[-log( )] are given by
)] are given by
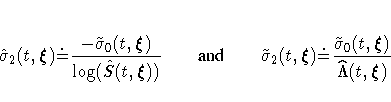
respectively.
Let 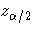 be the upper
be the upper 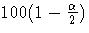 percentile point of the standard normal distribution.
A
percentile point of the standard normal distribution.
A 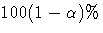 confidence interval for the survivor function
confidence interval for the survivor function
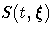 is given in the following table.
is given in the following table.
|
Method
|
CLTYPE
|
Confidence Limits
|
| LOG | PL | ![\exp[\log(\hat{S}(t,{\xi})) +- z_{\frac{\alpha}2}\tilde{\sigma}_{0}(t,{\xi})]](images/phreq166.gif) |
| LOG | CH | ![\exp[\log(\tilde{S}(t,{\xi})) +- z_{\frac{\alpha}2}\tilde{\sigma}_{0}(t,{\xi})]](images/phreq167.gif) |
| LOGLOG | PL | ![\exp\{-\exp[\log(-\log(\hat{S}(t,{\xi}))) +- z_{\frac{\alpha}2}\hat{\sigma}_{2}(t,{\xi})]\}](images/phreq168.gif) |
| LOGLOG | CH | ![\exp\{-\exp[\log(-\log(\tilde{S}(t,{\xi}))) +- z_{\frac{\alpha}2}\tilde{\sigma}_{2}(t,{\xi})]\}](images/phreq169.gif) |
| NORMAL | PL | 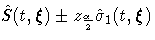 |
| NORMAL | CH | 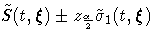 |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.
![{\cal L}=\prod_{i=0}^k
\{ \prod_{l \in {\cal D}_i}
( [S_{0}(t_{i})]^{ {\rm exp...
... )
\prod_{l \in {\cal C}_i} [S_{0}(\gamma_{l}+0)]^{{\rm exp}(z'_{l}{\beta})}
\}](images/phreq136.gif)
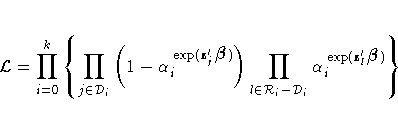
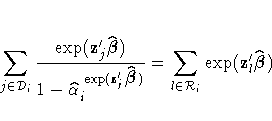
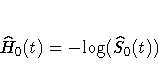
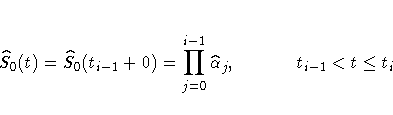
![]() ,the product-limit estimate of the survival function at
,the product-limit estimate of the survival function at ![]() is
is
![\hat{S}(t,{\xi})= [\hat{S}_{0}(t)]^{\exp({\beta}'{\xi})}](images/phreq152.gif)
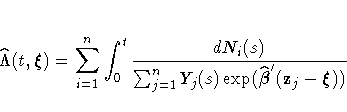
![& &\hat{var}\{n^{\frac{1}2}(\hat{\Lambda}(t,{\xi}) -
\Lambda(t,{\xi}))\} \ & = ...
...i}))]^2} + \biggr.
\biggl. H'(t,{\xi})\hat{V}(\hat{{\beta}})H(t,{\xi}) \biggr\}](images/phreq155.gif)
![H(t,{\xi}) = \sum_{i=1}^n\int_{0}^t
\frac{\sum_{l=1}^n Y_{l}(s)(Z_{l}-{\xi})\ex...
...{\xi}))}
{[\sum_{j=1}^n Y_{j}(s)\exp(\hat{{\beta}}'(z_{j} - {\xi}))]^2} dN_i(s)](images/phreq157.gif)
![]() is
is
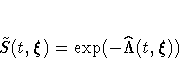
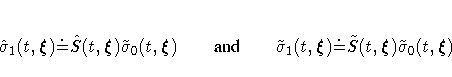
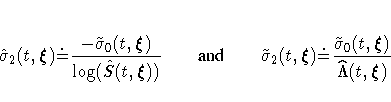
![]() be the upper
be the upper ![]() percentile point of the standard normal distribution.
A
percentile point of the standard normal distribution.
A ![]() confidence interval for the survivor function
confidence interval for the survivor function
![]() is given in the following table.
is given in the following table.