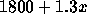 .
.
- For x=2000 the mean becomes 4400. The probability that 28
day strength is more than 5000 is the probability that a standard
normal variate is more than (5000-4400)/350=1.71. This probability is
0.0436.
- For x=2500 the mean is 5050 and the probability is the
area to the right of -50/350 which is 0.556.
- Let
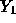 be the observation at x=2500 and
be the observation at x=2500 and  the observation
x=2000. Then the mean of
the observation
x=2000. Then the mean of  is 1.3(500)=650 while the SD of the
difference is
is 1.3(500)=650 while the SD of the
difference is  . The probability we want is that
a standard normal is more than (1000-650)/495=0.707.This is roughly 0.24.
. The probability we want is that
a standard normal is more than (1000-650)/495=0.707.This is roughly 0.24.
- Now
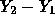 is normal with mean
is normal with mean 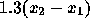 and SD 495. We want
the probability that
and SD 495. We want
the probability that 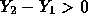 or the probability to the right of
or the probability to the right of
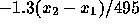 to be 0.95. This means that
to be 0.95. This means that 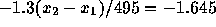 or
or 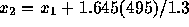 . The answer is then 626.
. The answer is then 626.
options pagesize =60 linesize=80;
data q16;
infile 'q16.dat';
input x y;
proc reg;
model y=x;
plot residual.*predicted.;
plot y*x;
run;
The output for the full data set is
Dependent Variable: Y
Analysis of Variance
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Prob>F
Model 1 538208.57051 538208.57051 385.024 0.0001
Error 4 5591.42949 1397.85737
C Total 5 543800.00000
Root MSE 37.38793 R-square 0.9897
Dep Mean 560.00000 Adj R-sq 0.9871
C.V. 6.67642
Parameter Estimates
Parameter Standard T for H0:
Variable DF Estimate Error Parameter=0 Prob > |T|
INTERCEP 1 137.875631 26.37756553 5.227 0.0064
X 1 9.311567 0.47454663 19.622 0.0001
----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+----
RESIDUAL | |
| |
50 + +
| |
| |
| 1 |
| |
40 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
30 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
20 + 1 +
| |
| |
| |
R | 1 |
e 10 + +
s | |
i | |
d | 1 |
u | |
a 0 + +
l | |
| |
| |
| |
-10 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
-20 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
-30 + +
| |
| |
| |
| 1 |
-40 + 1 +
| |
| |
----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+----
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200
Predicted Value of Y PRED
----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+----
Y | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
1200 + 1 +
| |
| |
| |
1100 + +
| |
| |
| |
1000 + +
| |
| |
| |
900 + +
| |
| |
| |
800 + +
| |
| |
| |
700 + +
| |
| |
| |
600 + +
| |
| 1 |
| |
500 + 1 +
| 1 |
| |
| |
400 + +
| |
| 1 |
| |
300 + +
| 1 |
| |
| |
200 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+----
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
X
while that for the edited data set is
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Prob>F
Model 1 49839.81693 49839.81693 61.274 0.0043
Error 3 2440.18307 813.39436
C Total 4 52280.00000
Root MSE 28.52007 R-square 0.9533
Dep Mean 432.00000 Adj R-sq 0.9378
C.V. 6.60187
Parameter Estimates
Parameter Standard T for H0:
Variable DF Estimate Error Parameter=0 Prob > |T|
INTERCEP 1 190.352403 33.40167361 5.699 0.0107
X 1 7.551487 0.96470574 7.828 0.0043
-+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+--
RESIDUAL | |
| |
| |
| |
30 + 1 +
| |
| |
| |
| 1 |
| |
| |
20 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
10 + +
| |
| |
R | |
e | |
s | |
i | |
d 0 + +
u | |
a | |
l | |
| |
| |
| |
-10 + +
| |
| |
| |
| 1 1 |
| |
| |
-20 + +
| |
| 1 |
| |
| |
| |
| |
-30 + +
| |
| |
| |
-+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+--
280 300 320 340 360 380 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540
Predicted Value of Y PRED
-----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+-----
600 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| 1 |
550 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
500 + 1 +
| |
| |
Y | |
| 1 |
| |
| |
450 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
400 + +
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
350 + 1 +
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
300 + +
| |
| |
| 1 |
| |
| |
| |
250 + +
-----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+-----
12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0 22.5 25.0 27.5 30.0 32.5 35.0 37.5 40.0 42.5 45.0
X
- The scatter plot for the full data set seems reasonable.
- The regression equation is
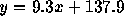 .
.
- This just asks for
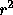 but I doubt the utility of the
calculation unless the x levels were set by random sampling of
pairs. The value is 0.99.
but I doubt the utility of the
calculation unless the x levels were set by random sampling of
pairs. The value is 0.99.
- There are many ways to compare the two lines. One is based on
examining the difference in fitted slopes: 9.31 compared to 7.55 with
a standard error of either about 0.47 or 1. This is not actually a
significant difference assuming the model holds. Another approach is
suggested in the text. The predicted value of Y when x is 112 is,
for the second line 7.55(112)+190.4 or about 1036. The standard deviation
of
 is given on page 503 and you could carry
out a t-test using
is given on page 503 and you could carry
out a t-test using 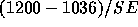 and getting P-values from the
t-distribution on 3 degrees of freedom.
and getting P-values from the
t-distribution on 3 degrees of freedom.
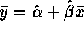 . The right hand side is
. The right hand side is 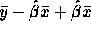 which is evidently
which is evidently 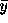 .
.
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Prob>F
Model 1 8.17906 8.17906 674.982 0.0001
Error 8 0.09694 0.01212
C Total 9 8.27600
Root MSE 0.11008 R-square 0.9883
Dep Mean 3.92000 Adj R-sq 0.9868
C.V. 2.80814
Parameter Estimates
Parameter Standard T for H0:
Variable DF Estimate Error Parameter=0 Prob > |T|
INTERCEP 1 2.141648 0.07679262 27.889 0.0001
X 1 0.006801 0.00026176 25.980 0.0001
- The output gives the estimated standard error of the slope as
0.077 and the square root of the mean squared error as 0.11.
- The test is based on
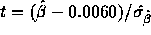 which is 3.06. You get a
P-value from t tables on 8 degrees of freedom and conclude
that the slope is not 0.0060 (
which is 3.06. You get a
P-value from t tables on 8 degrees of freedom and conclude
that the slope is not 0.0060 (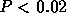 two tailed).
two tailed).
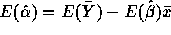 (in my
notation). You are allowed to assume that
(in my
notation). You are allowed to assume that 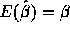 . Now
. Now
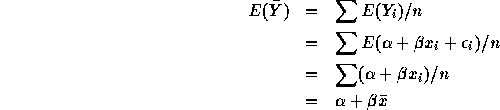
Putting the two pieces we get 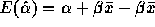 which is just
which is just  .
.
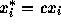 and
and 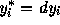 . The fitted slope
based on the starred data is
. The fitted slope
based on the starred data is
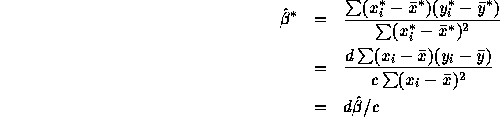
The estimated standard error 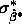 of
of 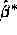 is
is

To evaluate this note first that 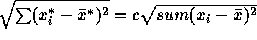 . Next
. Next
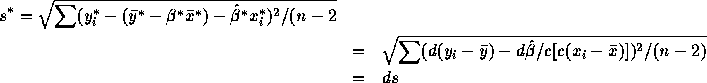
Assembling the pieces shows that
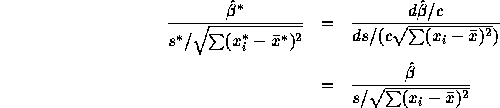
- The test statistic is
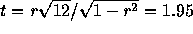 on 12
degrees of freedom. For a two sided test I get P a bit over 0.10
and conclude that there is only quite weak evidence fo a correlation
between content and gas porosity.
on 12
degrees of freedom. For a two sided test I get P a bit over 0.10
and conclude that there is only quite weak evidence fo a correlation
between content and gas porosity.
- The percent variance explained is
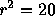 %.
%.
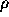 must be either
0.16 or -0.16 which is a pretty weak correlation.)
must be either
0.16 or -0.16 which is a pretty weak correlation.)
Sum of Mean
Source DF Squares Square F Value Prob>F
Model 1 25.62223 25.62223 17.604 0.0057
Error 6 8.73277 1.45546
C Total 7 34.35500
Root MSE 1.20643 R-square 0.7458
Dep Mean 77.72500 Adj R-sq 0.7034
C.V. 1.55217
Parameter Estimates
Parameter Standard T for H0:
Variable DF Estimate Error Parameter=0 Prob > |T|
INTERCEP 1 81.173057 0.92589886 87.669 0.0001
X 1 -0.133258 0.03176040 -4.196 0.0057
- The fitted line is
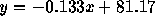 .
.
- This question asks you to test the hypothesis that the
true slope is 0. The P value is 0.0057 from the output so that the
hypothesis of no relation between x and Y is rejected.
- The standard error of
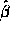 is inversely proportional
to
is inversely proportional
to  . Putting 4 data points at 0 and 4 at
50 makes
. Putting 4 data points at 0 and 4 at
50 makes 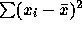 equal to 5000 while the value for
the data set is only about 1450.
Thus the new design estimates
equal to 5000 while the value for
the data set is only about 1450.
Thus the new design estimates  more precisely.
Using only 3 points at 0 and at 50 gives a sum of 3750 which is still much
more precise than the design used.
more precisely.
Using only 3 points at 0 and at 50 gives a sum of 3750 which is still much
more precise than the design used.
- You are supposed to plug 25 into the regression equation and then
use the formulas on page 503 to attach a standard error to this number.
You get 77.85 with an estimated standard error of 0.428. This does not
really answer the question about whether or not efficiency has been
precisely estimated but that seems to be something of a judgement.
General Linear Models Procedure
R-Square C.V. Root MSE Y Mean
0.070002 26.22198 198.15080 755.66667
T for H0: Pr > |T| Std Error of
Parameter Estimate Parameter=0 Estimate
INTERCEPT 684.4057037 5.78 0.0007 118.3236387
X 14.8804795 0.73 0.4915 20.5000646
The test statistic is 0.73 with 7 degrees of freedom. Since the test is one
sided we get a P value of 0.4915/2 which is certainly not significant.
Thus it seems quite possible that there is no (linear) relation between
eye weight and thickness.
- Since
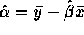 it clearly suffices to
check that
it clearly suffices to
check that 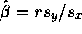 . But this last value is
. But this last value is
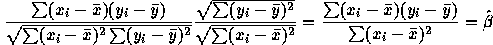
as required.
- You need to compute r and that's the answer except that if r is
negative then for each SD below average on x you predict that r times
that many SD's above average on y while the deviations are in the same
direction if r is positive.
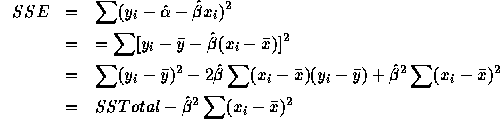
Divide through by SSTotal and use the formula 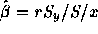 where
where 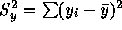 , etc., to get
, etc., to get
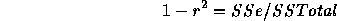
Then
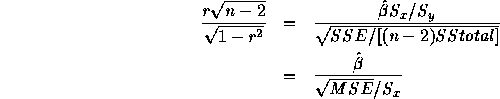
which is the usual t-statistic. Note the use of the fact that 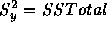 .
.