options pagesize=60 linesize=80;
data scenic;
infile 'scenic.dat' firstobs=2;
input Stay Age Risk Culture Chest Beds School
Region Census Nurses Facil;
Nratio = Nurses / Census ;
R1 = -(Region-4)*(Region-3)*(Region-2)/6;
R2 = (Region-4)*(Region-3)*(Region-1)/2;
R3 = -(Region-4)*(Region-2)*(Region-1)/2;
S1 = School-1;
proc reg data=scenic;
model Risk = S1 Culture Stay Nurses Nratio { R1 R2 R3 }
Chest Beds Census Facil / selection=stepwise
groupnames = 'School' 'Culture' 'Stay' 'Nurses' 'Nratio'
'Region' 'Chest' 'Beds' 'Census' 'Facil';
run ;
EDITED SAS OUTPUT (Complete output)
Stepwise Procedure for Dependent Variable RISK
Step 1 Group Culture Entered R-square=0.312659 C(p)=58.3641
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP 3.19789965 0.19376813 339.64905575 272.37 0.0001
--- Group Culture -- 62.96314170 50.49 0.0001
CULTURE 0.07325862 0.01030975 62.96314170 50.49 0.0001
-----------------------------------------------------------
Step 2 Group Stay Entered R-square=0.45040256 C(p)=26.82419
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP 0.80549102 0.48775579 2.74400250 2.73 0.1015
--- Group Culture --- 33.39687778 33.19 0.0001
CULTURE 0.05645147 0.00979843 33.39687778 33.19 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 27.73884588 27.57 0.0001
STAY 0.27547211 0.05246473 27.73884588 27.57 0.0001
-----------------------------------------------------------
Step 3 Group Facil Entered R-square = 0.4934 C(p)=18.3545
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP 0.49133226 0.48163614 0.97401801 1.04 0.3099
--- Group Culture --- 30.59827862 32.69 0.0001
CULTURE 0.05419997 0.00947933 30.59827862 32.69 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 16.47664606 17.60 0.0001
STAY 0.22390748 0.05336561 16.47664606 17.60 0.0001
--- Group Facil --- 8.65883687 9.25 0.0029
FACIL 0.01963027 0.00645392 8.65883687 9.25 0.0029
---------------------------------------------------------
Step 4 Group Nratio Entered R-square=0.52548 C(p)=12.5433
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP -0.49505513 0.59376426 0.61507231 0.70 0.4063
--- Group Culture --- 22.84513509 25.82 0.0001
CULTURE 0.04818092 0.00948204 22.84513509 25.82 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 21.44995791 24.24 0.0001
STAY 0.26758404 0.05434637 21.44995791 24.24 0.0001
--- Group Nratio --- 6.46014750 7.30 0.0080
NRATIO 0.79262357 0.29333869 6.46014750 7.30 0.0080
--- Group Facil --- 6.75349077 7.63 0.0067
FACIL 0.01747585 0.00632554 6.75349077 7.63 0.0067
---------------------------------------------------------
Step 5 Group Chest Entered R-square=0.53792 C(p)=11.513
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP -0.76804342 0.61022741 1.37763165 1.58 0.2109
--- Group Culture --- 16.71979631 19.23 0.0001
CULTURE 0.04318856 0.00984976 16.71979631 19.23 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 14.43814950 16.60 0.0001
STAY 0.23392650 0.05741114 14.43814950 16.60 0.0001
--- Group Nratio --- 4.38883521 5.05 0.0267
NRATIO 0.67240318 0.29931440 4.38883521 5.05 0.0267
--- Group Chest --- 2.50619510 2.88 0.0925
CHEST 0.00917860 0.00540681 2.50619510 2.88 0.0925
--- Group Facil --- 7.45710068 8.57 0.0042
FACIL 0.01843860 0.00629673 7.45710068 8.57 0.0042
---------------------------------------------------------
Step 6 Group Region Entered R-square=0.56826 C(p)=10.1269
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP -0.66156855 0.68931767 0.77004723 0.92 0.3394
--- Group Culture --- 19.41848300 23.23 0.0001
CULTURE 0.04717749 0.00978882 19.41848300 23.23 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 18.64724032 22.31 0.0001
STAY 0.28408192 0.06015054 18.64724032 22.31 0.0001
--- Group Nratio --- 1.86769604 2.23 0.1380
NRATIO 0.47735146 0.31936579 1.86769604 2.23 0.1380
--- Group Region --- 6.10861501 2.44 0.0689
R1 -0.91152625 0.33831556 6.06877293 7.26 0.0082
R2 -0.61170886 0.30630883 3.33408744 3.99 0.0484
R3 -0.54005754 0.30531855 2.61565335 3.13 0.0799
--- Group Chest --- 3.10587423 3.72 0.0566
CHEST 0.01029102 0.00533912 3.10587423 3.72 0.0566
--- Group Facil --- 7.66252029 9.17 0.0031
FACIL 0.01883340 0.00622080 7.66252029 9.17 0.0031
--------------------------------------------------------
Step 7 Group School Entered R-square=0.5783 C(p)= 9.68028
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP -1.29313397 0.79443852 2.18445103 2.65 0.1066
--- Group School --- 2.02343484 2.45 0.1203
S1 0.45874175 0.29282732 2.02343484 2.45 0.1203
--- Group Culture --- 21.14238169 25.64 0.0001
CULTURE 0.05016596 0.00990650 21.14238169 25.64 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 19.90843811 24.15 0.0001
STAY 0.29583936 0.06020399 19.90843811 24.15 0.0001
--- Group Nratio --- 1.42881407 1.73 0.1909
NRATIO 0.42026288 0.31924279 1.42881407 1.73 0.1909
--- Group Region --- 7.09035688 2.87 0.0402
R1 -0.99737538 0.34041455 7.07745167 8.58 0.0042
R2 -0.64425716 0.30489819 3.68115979 4.46 0.0370
R3 -0.59950685 0.30557155 3.17349874 3.85 0.0525
--- Group Chest --- 2.85453005 3.46 0.0656
CHEST 0.00987802 0.00530873 2.85453005 3.46 0.0656
--- Group Facil --- 9.68526975 11.75 0.0009
FACIL 0.02391008 0.00697611 9.68526975 11.75 0.0009
----------------------------------------------------------
Step 8 Group Nratio Removed R-square=0.57121 C(p)=9.40791
Parameter Standard Type II
Variable Estimate Error Sum of Squares F Prob>F
INTERCEP -0.83240584 0.71570292 1.12313185 1.35 0.2475
--- Group School --- 2.46231681 2.97 0.0880
S1 0.50274483 0.29193670 2.46231681 2.97 0.0880
--- Group Culture --- 23.66688888 28.50 0.0001
CULTURE 0.05233635 0.00980270 23.66688888 28.50 0.0001
--- Group Stay --- 18.47964968 22.26 0.0001
STAY 0.27469386 0.05822575 18.47964968 22.26 0.0001
--- Group Region --- 9.68716458 3.89 0.0111
R1 -1.10696516 0.33123989 9.27275385 11.17 0.0012
R2 -0.76673818 0.29137725 5.74922078 6.92 0.0098
R3 -0.75936643 0.28139304 6.04647398 7.28 0.0081
--- Group Chest --- 3.92124933 4.72 0.0320
CHEST 0.01132621 0.00521177 3.92124933 4.72 0.0320
--- Group Facil --- 11.30278424 13.61 0.0004
FACIL 0.02545939 0.00690031 11.30278424 13.61 0.0004
----------------------------------------------------------
All groups of variables left in the model are
significant at the 0.1500 level. No other group
of variables met the 0.1500 significance level for
entry into the model.
Summary of Stepwise Procedure for Dependent Variable RISK
Group Number Partial Model
Step Entered Removed In R**2 R**2 C(p) F Prob>F
1 Culture 1 0.3127 0.3127 58.3641 50.4918 0.0000
2 Stay 2 0.1377 0.4504 26.8242 27.5690 0.0000
3 Facil 3 0.0430 0.4934 18.3545 9.2513 0.0029
4 Nratio 4 0.0321 0.5255 12.5433 7.3012 0.0080
5 Chest 5 0.0124 0.5379 11.5130 2.8818 0.0925
6 Region 8 0.0303 0.5683 10.1269 2.4357 0.0689
7 School 9 0.0100 0.5783 9.6803 2.4542 0.1203
8 Nratio 8 0.0071 0.5712 9.4079 1.7330 0.1909
COMMENTS ON OUTPUT



Up to now our theory has been used to compute P-values or fix
critical points to get desired ![]() levels. We have assumed that
all our null hypotheses are True. I now discuss power or Type II error
rates of our tests. Read Chapter 26, section 4, 5 and 6.
levels. We have assumed that
all our null hypotheses are True. I now discuss power or Type II error
rates of our tests. Read Chapter 26, section 4, 5 and 6.
Consider a t-test of ![]() .
The test statistic is
.
The test statistic is

![\begin{displaymath}\frac{\hat\beta_k/\left[\sigma\sqrt{(X^TX)^{-1}_{kk}}\right]}{
\sqrt{[ SSE/\sigma^2]/(n-p)}}\end{displaymath}](img20.gif)
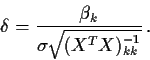
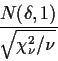
Table B.5 on page 1346 gives the probability that the absolute
value of a non-central t exceeds a given level. If we take the level
to be the critical point for a t test at some level ![]() then
the probability we look up is the corresponding power, that is,
the probability of rejection. Notice that the power depends on
two unknown quantities,
then
the probability we look up is the corresponding power, that is,
the probability of rejection. Notice that the power depends on
two unknown quantities, ![]() and
and ![]() and on 1 quantity
which is sometimes under the experimenter's control (in a designed
experiment) and sometimes not (as in an observational study.)
and on 1 quantity
which is sometimes under the experimenter's control (in a designed
experiment) and sometimes not (as in an observational study.)
Same idea applies to any linear statistic of the form
![]() - you get a non-central t distribution on
the alternative. So, for example, if testing
- you get a non-central t distribution on
the alternative. So, for example, if testing
![]() but in fact
but in fact
![]() the non-centrality parameter is
the non-centrality parameter is

Before an experiment is run it is sensible, if the experiment is
costly, to try to work out whether or not it is worth doing. You
will nly do an experiment if the probability of Type I and II errors
are both reasonably low.
The simplest case arises when you prespecify a level, say
![]() and an acceptable probability of Type II error,
and an acceptable probability of Type II error,
![]() say 0.10. Then you need to specify
say 0.10. Then you need to specify

The simplest example of the power of an F test arises in regression through the
origin (that is, a model with no intercept term.) Consider the model
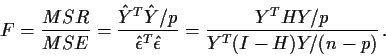

The numerator, however, is

FACT:
If W is a
![]() random vector and Q is idempotent with rank pthen WTQW has a non-central
random vector and Q is idempotent with rank pthen WTQW has a non-central
![]() distribution with non-centrality parameter
distribution with non-centrality parameter
FACT
If U and V are independent ![]() variables with degrees of freedom
variables with degrees of freedom
![]() and
and ![]() ,
V is central and U is non-central with non-centrality
parameter
,
V is central and U is non-central with non-centrality
parameter ![]() then
then
POWER CALCULATIONS
Table B 11 gives powers of F tests for various small numerator
degrees of freedom and a range of denominator degrees of freedom for
![]() or
or
![]() .
In the table
.
In the table ![]() is simply our
is simply our
![]() (that is, the square root of what I called the non-centrality parameter
divided by the square root of 1 more than the numerator degrees of freedom.)
(that is, the square root of what I called the non-centrality parameter
divided by the square root of 1 more than the numerator degrees of freedom.)
SAMPLE SIZE CALCULATIONS
Sometimes done with charts and sometimes with tables; see table B 12.
This table depends on a quantity
