Definition: If
![]() is a white noise series and
is a white noise series and ![]() and
and
![]() are constants then
are constants then
Question: From observations on X can we estimate the
b's and
![]() accurately? NO.
accurately? NO.
Definition: A model for data X is a family
![]() of possible distributions for X.
of possible distributions for X.
Definition: A model is identifiable if
![]() implies
that
implies
that
![]() ;
that is different
;
that is different ![]() 's
give different distributions for the data.
's
give different distributions for the data.
When a model is unidentifiable there are different values of ![]() which make exactly the same predictions about the data so the data
do not permit you to distinguish between these
which make exactly the same predictions about the data so the data
do not permit you to distinguish between these ![]() values.
values.
Example: Suppose ![]() is an iid
is an iid
![]() series and that
series and that
![]() .
Then the series X has
mean 0 and covariance
.
Then the series X has
mean 0 and covariance




You should notice two things:


The two solutions multiply together to
give the constant term 1 in the quadratic equation. If the two roots
are distinct it follows that one of them is larger than 1 and the other
smaller in absolute value. Let b and b* denote the two roots.
Let
![]() and
and
![]() .
Let
.
Let
![]() be
iid
be
iid
![]() and
and
![]() be iid
be iid
![]() .
Then
.
Then
Reason: We can manipulate the model equation for Xjust as we did for and autoregressive process last time:
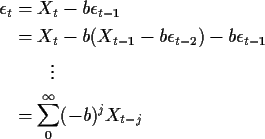
This manipulation makes sense if |b| < 1. If so then we can
rearrange the equation to get

If, on the other hand, |b| > 1 then we can write


Definition: An MA(p) process is invertible if it can be written in the form

Definition: A process X is an autoregression of order p (written AR(p))
if

Definition: The backshift operator transforms a time series into another
time series by shifting it back one time unit; if X is a time series
then BX is the time series with
Now we use B to develop a formal method for studying the
existence of a given AR(p) and the invertibility of
a given MA(p). An AR(1) process satisfies
If b is a real number then




Now consider a general AR(p) process:






(Asymptotically stationary means this: if you make
![]() anything at all and use the equation defining the AR(p)to define all the rest of the X values then as
anything at all and use the equation defining the AR(p)to define all the rest of the X values then as
![]() the process
gets closer to being stationary. The assertion of asymptotic stationarity
is equivalent here to the existence of an exactly stationary solution
of the equations.)
the process
gets closer to being stationary. The assertion of asymptotic stationarity
is equivalent here to the existence of an exactly stationary solution
of the equations.)
Definition: A process X is an ARMA(p,q) (mixed autoregressive of order pand moving average of order q) if it satisfies


The ideas we used above can be stretched to show that the process X is
identifiable and causal (can be written as an infinite order
autoregression on the past) if the roots of ![]() lie outside the
unit circle. A stationary solution, which can be written as an infinite
order causal (no future
lie outside the
unit circle. A stationary solution, which can be written as an infinite
order causal (no future ![]() s in the average) moving average, exists
if all the roots of
s in the average) moving average, exists
if all the roots of ![]() lie outside the unit circle.
lie outside the unit circle.
Other Stationary Processes:
A Poisson process is a process N(A) indexed by subsets A of the
real line with the property that each N(A) has a Poisson distribution
with parameter
![]() and if
and if
![]() are any non-overlapping subsets of R then
are any non-overlapping subsets of R then
![]() are independent. We often use N(t) for
N([0,t]).
are independent. We often use N(t) for
N([0,t]).
To define a shot noise process we let X(t) =1 at those t where
there is a jump in N and 0 elsewhere. The process X is stationary.
If we have some function g defined on
![]() and decreasing
sufficiently quickly to 0 (like say
g(x) =e-x) then the process
and decreasing
sufficiently quickly to 0 (like say
g(x) =e-x) then the process