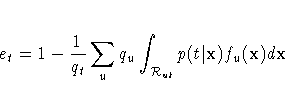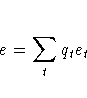Posterior Probability Error-Rate Estimates
The posterior probability error-rate estimates (Fukunaga and Kessell
1973; Glick 1978; Hora and Wilcox 1982) for each group are based on
the posterior probabilities of the observations classified into that
same group.
A sample of observations with classification results
can be used to estimate the posterior error rates.
The following notation is used to describe the sample.
- S
- the set of observations in the (training) sample
- n
- the number of observations in S
- nt
- the number of observations in S in group t
- Rt
- the set of observations such that the posterior
probability belonging to group t is the largest
- Rut
- the set of observations from group u such that the
posterior probability belonging to group t is the largest.
The classification error rate for group t is defined as

The posterior probability of x
for group t can be written as

where  is the unconditional density of x.
is the unconditional density of x.
Thus, if you replace ft(x) with
 , the error rate is
, the error rate is

An estimator of et, unstratified over the groups
from which the observations come, is then given by

where  is estimated from the classification
criterion, and the summation is over all sample
observations of S classified into group t.
The true group membership of each observation
is not required in the estimation. The term nqt is the number of
observations that are expected to be classified into group t,
given the priors. If more observations than expected are classified
into group t, then
is estimated from the classification
criterion, and the summation is over all sample
observations of S classified into group t.
The true group membership of each observation
is not required in the estimation. The term nqt is the number of
observations that are expected to be classified into group t,
given the priors. If more observations than expected are classified
into group t, then  can be negative.
can be negative.
Further, if you replace f(x) with
 , the error rate can be written as
, the error rate can be written as
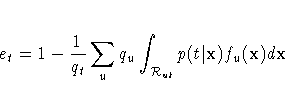
and an estimator stratified over the group
from which the observations come is given by

The inner summation is over all sample observations of
S coming from group u and classified into group t,
and nu is the number of observations originally from group u.
The stratified estimate uses only the
observations with known group membership.
When the prior probabilities of the group membership
are proportional to the group sizes, the stratified
estimate is the same as the unstratified estimator.
The estimated group-specific error rates can be less
than zero, usually due to a large discrepancy between
prior probabilities of group membership and group sizes.
To have a reliable estimate for group-specific error rate
estimates, you should use group sizes that are at least approximately
proportional to the prior probabilities of group membership.
A total error rate is defined as a weighted
average of the individual group error rates
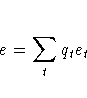
and can be estimated from

or

The total unstratified error-rate estimate can also be written as

which is one minus the average value of the maximum
posterior probabilities for each observation in the sample.
The prior probabilities of group membership do
not appear explicitly in this overall estimate.
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.