Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The PHREG Procedure |
The LD statistic
approximates the likelihood displacement, which
is the amount by which minus twice the
log likelihood (![]() ), under a fitted model,
changes when each subject in turn is left out. When the ith
subject is omitted, the likelihood displacement is
), under a fitted model,
changes when each subject in turn is left out. When the ith
subject is omitted, the likelihood displacement is
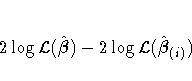
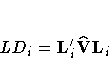
This approximation is output to the LD= variable.
The LMAX statistic is another global influence statistic. This statistic is based on the symmetric matrix
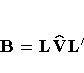
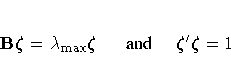
When the counting process MODEL specification is used, the LD= and LMAX= variables are set to missing, because these two global influence statistics can be calculated on a per subject basis only.
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.