SPEECH ACOUSTICS
(click on
the capital letter for your answer)
1. Sounds produced by the vibration of the
vocal folds are said to be _________ and thus are
characterized as having a(n) ________.
First blank
|
A.
voiced
|
B. unvoiced
|
C. stopped
|
D. rolled
|
Second blank
|
A.
spectrum
|
B. pitch
|
C. envelope
|
D. narrow
band spectrum
|
2. The
vowel is characterized by energy peaks called __________
that correspond to a specific configuration of the vocal
tract.
A.
harmonics
|
B.
formants
|
C. bands
|
D. partials
|
3. The
energy peaks in the vowels are an example of a(n)
__________.
A.
harmonic
|
B.
inharmonic
|
C.
resonance
|
D. noise
band
|
4. The
pure vowels may be placed in the vowel quadrilateral
according to tongue position. T or F
5. The
eight cardinal vowels occupy the boundaries of the vowel
quadrilateral. T or F
6. The vowels found in words such as "tone, take, might,
shout toil" are called __________.
A. pure
vowels
|
B.
cardinal vowels |
C.
formants
|
D.
diphthongs
|
7. Vowel
formants change with pitch inflections. T or F
8. Consonants
are always unvoiced since they are characterized as
being noise bands. T or F
9.
Consonants such as p, b, t, g are called _________,
whereas those such as f, v, th, sh are called
____________.
First blank
|
A. nasal
|
B.
fricative |
C.
liquid
|
D.
plosive
|
Second blank
|
A.
nasal
|
B.
fricative
|
C.
liquid |
D.
plosive
|
10. Sibilants always have their energy
centred in the range _________.
A.
100-250 Hz
|
B.
500-1000 Hz
|
C. 1-4
kHz
|
D.
5-10 kHz
|
11. Speech
will be largely unintelligible if it is missing energy
in the ___________ range, whereas the fundamental of
the voice is pitched in the _________ range.
First blank
|
A.
100-250 Hz
|
B.
500-1000 Hz |
C.
1-4 kHz
|
D.
5-10 kHz
|
Second blank
|
A.
100-250 Hz
|
B.
500-1000 Hz
|
C.
1-4 kHz |
D.
5-10 kHz
|
12.
Normal speech has an intensity of around ________.
A.
30-35 dB
|
B.
40-50 dB
|
C.
55-65 dB
|
D.
75-85 dB
|
13. A whispered sound may be said to be _______ .
A.
voiced
|
B.
unvoiced
|
C.
stopped
|
D. a
fricative
|
14. The singing formant is in the range _________.
A.
100-250 Hz
|
B.
500-1000 Hz
|
C. 2-3
kHz
|
D. 5-10
kHz
|
15. The
changing pitch pattern in the spoken voice is called
________.
A.
inflection
|
B.
paralanguage
|
C.
dynamics
|
D.
a diphthong
|
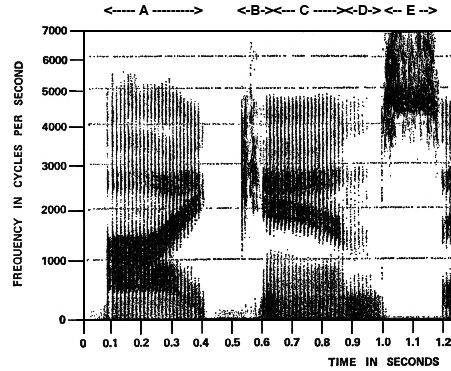
16.-20. In
the spectrogram below, match phoneme areas A, B,
C, D and E (indicated at the top) with the
following list.
16. Phoneme
A
|
a.
vowel
|
b.
consonant
|
c.
sibilant
|
d.
nasal
|
e.
diphthong
|
17. Phoneme
B
|
a.
vowel
|
b.
consonant
|
c.
sibilant
|
d.
nasal
|
e.
diphthong
|
18. Phoneme
C
|
a.
vowel
|
b.
consonant
|
c.
sibilant
|
d.
nasal
|
e.
diphthong
|
19. Phoneme
D
|
a.
vowel
|
b.
consonant
|
c.
sibilant
|
d.
nasal
|
e.
diphthong
|
20. Phoneme
E
|
a.
vowel
|
b.
consonant
|
c.
sibilant
|
d.
nasal
|
e.
diphthong
|
Index
home