Reading for Today's Lecture: Chapters 1, 2 and 3 of Ross.
Goals of Today's Lecture:
Example 1: Three cards: one red on both sides, one black on both sides, one black on one side, red on the other. Shuffle, pick card at random. Side up is Black. What is the probability the side down is Black?
Solution: To do this carefully, enumerate sample space,
![]() ,
of all possible outcomes. Six sides to the three cards.
Label three red sides 1, 2, 3 with sides 1, 2 on the all red card (card
# 1).
Label three black sides 4, 5, 6 with 3, 4 on opposite sides of mixed
card (card #2). Define some events:
,
of all possible outcomes. Six sides to the three cards.
Label three red sides 1, 2, 3 with sides 1, 2 on the all red card (card
# 1).
Label three black sides 4, 5, 6 with 3, 4 on opposite sides of mixed
card (card #2). Define some events:

One representation
![]() .
Then
.
Then
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() and so on.
and so on.
Modelling: assumptions about some probabilities; deduce probabilities of other events. In example simplest model is
Apply two rules:
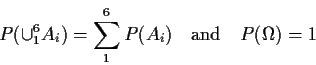
Definition of conditional probability:
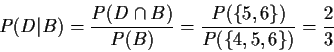
Example 2: Monte Hall, Let's Make a Deal. Monte shows you 3 doors. Prize hidden behind one. You pick a door. Monte opens a door you didn't pick; shows you no prize; offers to let you switch to the third door. Do you switch?