Publications
Below are selected works highlighting our most significant research contributions so far. For the full list of academic publications from our lab, go to our Google Scholar profile.

We introduce a dual-branch deep neural network, which combines the expansion path of the U-Net and original fully convolutional network, combined with a dilated network.
Da Ma, Donghuan Lu, Shuo Chen, Morgan Heisler, Setareh Dabiri, Sieun Lee, Hyunwoo Lee, Gavin Weiguang Ding, Marinko V. Sarunic, Mirza Faisal Beg
Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2021

To evaluate the performance of a federated learning framework for deep neural network-based retinal microvasculature segmentation and referable diabetic retinopathy (RDR) classification using optical coherence tomography (OCT) and OCT angiography (OCTA).
Julian Lo, Timothy T. Yu, Da Ma, Pengxiao Zang, Julia P. Owen, Qinqin Zhang, Ruikang K. Wang, Mirza Faisal Beg, Aaron Y. Lee, Yali Jia, Marinko V. Sarunic

We investigated differences due to sex in brain structural volume and cortical thickness in older cognitively normal (N=742), cognitively impaired (MCI; N=540) and Alzheimer’s Dementia (AD; N=402) individuals from the ADNI and AIBL datasets (861 Males and 823 Females). General linear models were used to control the effect of relevant covariates including age, intracranial volume, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner field strength and scanner types. Significant volumetric differences due to sex were observed within different cortical and subcortical regions of the cognitively normal group. The number of significantly different regions was reduced in the MCI group, and no region remained different in the AD group. Cortical thickness was overall thinner in males than females in the cognitively normal group, and likewise, the differences due to sex were reduced in the MCI and AD groups.
Oshin Sangha, Da Ma, Karteek Popuri, Jane Stocks, Lei Wang, Mirza Faisal Beg, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative

Our aim is to investigate patterns of brain glucose metabolism using fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in presymptomatic carriers of the C9orf72 repeat expansion to better understand the early preclinical stages of frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Structural MRI and FDG-PET were performed on clinically asymptomatic members of families with FTD caused by the C9orf72 repeat expansion (15 presymptomatic mutation carriers, C9orf72+; 20 non-carriers, C9orf72-). Regional glucose metabolism in cerebral and cerebellar gray matter was compared between groups.
Karteek Popuri, Mirza Faisal Beg, Hyunwoo Lee, Rakesh Balachandar, Lei Wang, Vesna Sossi, Claudia Jacova, Matt Baker, Elham Shahinfard, Rosa Rademakers, Ian RA Mackenzie, Ging-Yuek R Hsiung

Biomarkers for dementia of Alzheimer’s type (DAT) are sought to facilitate accurate prediction of the disease onset, ideally predating the onset of cognitive deterioration. T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a commonly used neuroimaging modality for measuring brain structure in-vivo, potentially providing information enabling the design of biomarkers for DAT.
Karteek Popuri, Da Ma, Lei Wang, Mirza Faisal Beg
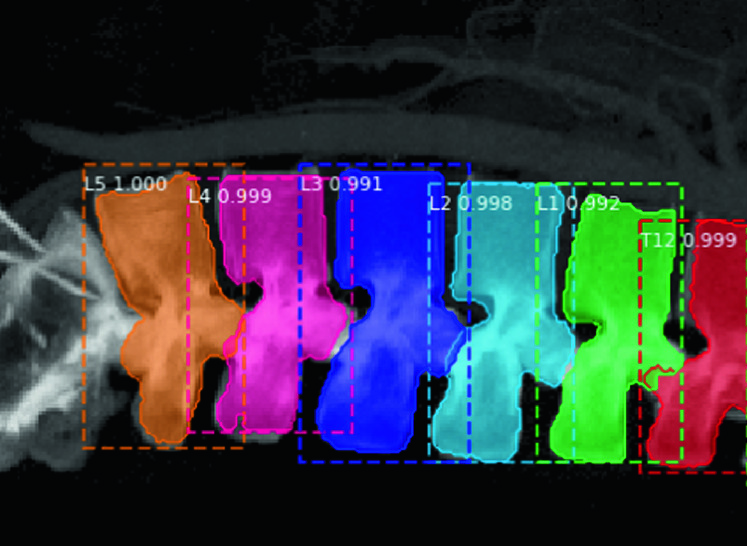
Spine disease is a growing problem in modern society and has been debilitating for every age-group. Researches have shown that more than 266 million people are facing degenerative spine disease and low back pain. CT scanning is a fast, painless, non-invasive diagnostic imaging modality that provides high spatial accuracy in obtaining the 3D structure of the vertebral. However, in real-life scenario, the clinic CT image might not cover the whole spine and the field of view might be hard to determine. Henceforth, this project aims to create and validate an automatic method that can detect, locate, and classify each vertebra from the partial field of view using deep learning. We used Mask R-CNN, a deep neural network aimed to solve the instance segmentation problem in machine learning or computer vision, and produce features such as bounding boxes, classes, and masks to identify each vertebra.
Renjie Wang, Jennifer Hui Yi Voon, Da Ma, Setareh Dabiri, Karteek Popuri, Mirza Faisal Beg
European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference, 2020
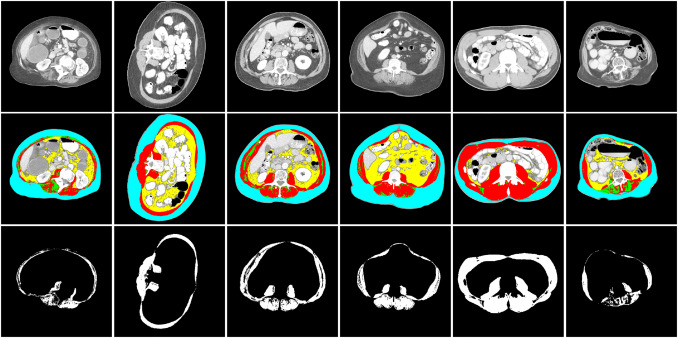
In diseases such as cancer, patients suffer from degenerative loss of skeletal muscle (cachexia). Muscle wasting and loss of muscle function/performance (sarcopenia) can also occur during advanced aging. Assessing skeletal muscle mass in sarcopenia and cachexia is therefore of clinical interest for risk stratification. In comparison with fat, body fluids and bone, quantifying the skeletal muscle mass is more challenging. Computed tomography (CT) is one of the gold standard techniques for cancer diagnostics and analysis of progression, and therefore a valuable source of imaging for in vivo quantification of skeletal muscle mass. In this paper, we design a novel deep neural network-based algorithm for the automated segmentation of skeletal muscle in axial CT images at the third lumbar (L3) and the fourth thoracic (T4) levels.
Setareh Dabiri, Karteek Popuri, Elizabeth M Cespedes Feliciano, Bette J Caan, Vickie E Baracos, Mirza Faisal Beg
Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2019

Retinal localization of amyloid-beta (A-beta) protein, the pathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), is not well understood. This study aims to describe A-beta localization in the post-mortem human retina from multiple spatial perspectives.
Qinyuan Alis Xu, Sieun Lee, Veronica Hirsch-Reinshagen, Ian Mackenzie, Robin Hsiung, Sijia Cao, Kailun Jiang, Marinko Sarunic, Mirza Faisal Beg, Jing Z Cui, Joanne A Matsubara
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2018