
Linguistics 322
Midterm Exam
Fall 1997
I. Why are the following sentences ungrammatical? (30)
(1 *Did Bill heard the tapes?
) a.
T lowers to V while Q is strong. Tense cannot be spelled out twice: once in V and once in C/T/V,
b. *Does swear at her rowdy customers Mindy?
Mindy has no Case, and the sentence has no subject.
c. [+Past] SEE BILL MARY.
No first or second pass to the lexicon, [+Past] not lowered, MARY has no Case, S has no subject.
II. Draw a Proposition-marker for the following sentences and derive the appropriate S-structure. Do not take any shortcuts--you may combine two steps into one diagram. Include features up to the S-structure where you may omit them: (40)
(2

Propositional Form (Logical Form)
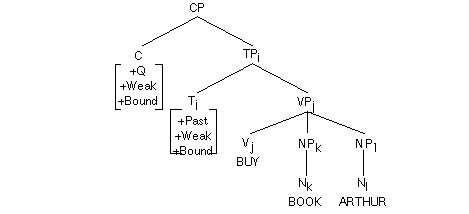
First Pass to the lexicon selects grammatical categories and grammatical features. (Indices are shown here but useful when agreement takes place)[.
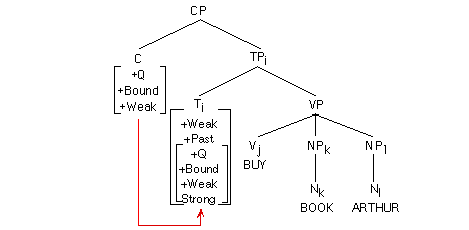
+Q] is bound. It lowers to T which is the only category that can function as a host for Q. Lowering is technically a copy of features lowered to some node. When Q is adjoined to T, it becomes strong as long as the sentence is a root sentence, and the subject is not a WH-word.
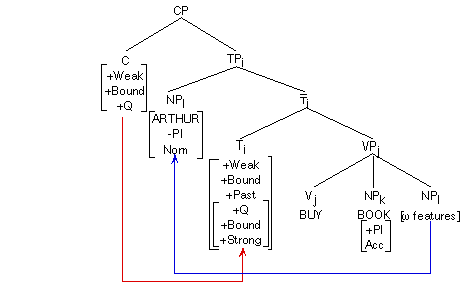
The direct complement of the verb BUY is assigned the accusative Case. The secondary complement of V remains Caseless. It must raise in search for Case, and the sentence needs a subject by the Extended Projection Principle. T (or more specifically, [+Past]) assigns the nominative Case to the subject.
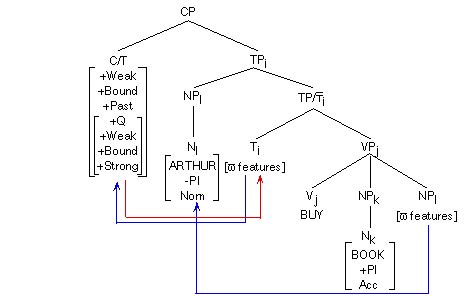
+Q is marked as [+Strong]. It must move back to its original position in the syntax.
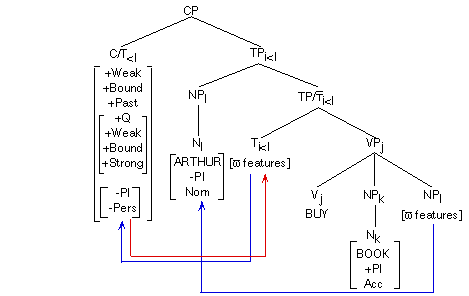
Agreement percolates the features of the subject (any modifier) onto TP and the features percolate down to T.
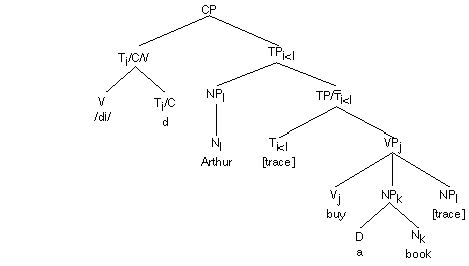
The morpheme (dummy verb) (DO) is inserted, and its splits into the stem /dî/ and the past tense suffix /d/. The other categories are spelled out. (Note, the indices on each category need not be included.)
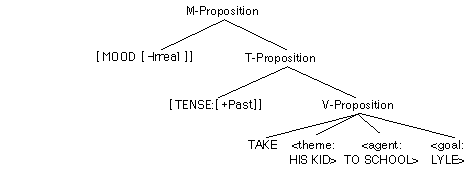
Propositional Form (Logical Form)
First pass to lexicon selects grammatical category and grammatical features.

The bound affix T lowers to acceptable host V.
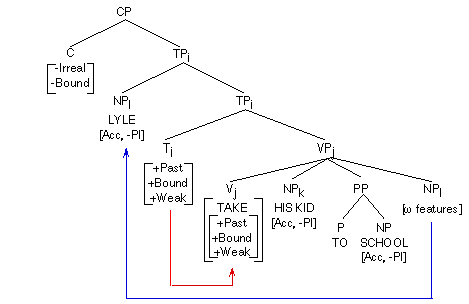
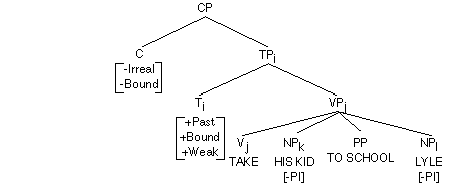
Accusative Case assigned to his kid by main verb, accusative Case to NP by P to, and remaining NP Lyle raises and adjoins to TP where assigned the nominative Case by T.

Agreement.
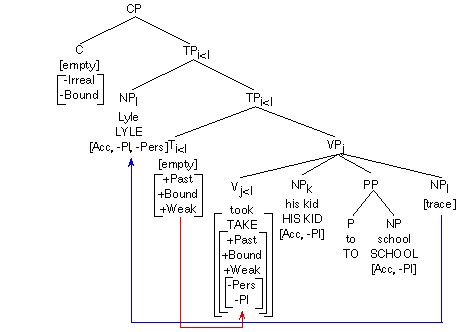
III. Explain the principles and the parameters you have selected for sentence See a) above. (10)
IV. What is the lexical entry for the verb read? (See back side of exam). Use the following sentences: (10)
(3 Ellen read a book.
) a.
b. Sam read a story to Jimmy.
c. Lottie reads a lot.
d. Polly reads to her children.
V. Which feature directly refers to the Unattached Affix Constraint? (5)
[+Bound]
VI. Which occurs first?--the first lexical pass or Lowering? (5)
The first lexical pass.
|
Inherent syntactic feature (just 1). (Hint: what is the inherent feature of an affix?) |