Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The EXPAND Procedure |
This example shows the interpolation of a series of values measured at irregular points in time. The data are hypothetical. Assume that a series of randomly timed quality control inspections are made and defect rates for a process are measured. The problem is to produce two reports: estimates of monthly average defect rates for the months within the period covered by the samples, and a plot of the interpolated defect rate curve over time.
The following statements read and print the input data, as shown in Output 11.2.1.
data samples;
input date : date9. defects @@;
label defects = "Defects per 1000 units";
format date date9.;
datalines;
13jan1992 55 27jan1992 73 19feb1992 84 8mar1992 69
27mar1992 66 5apr1992 77 29apr1992 63 11may1992 81
25may1992 89 7jun1992 94 23jun1992 105 11jul1992 97
15aug1992 112 29aug1992 89 10sep1992 77 27sep1992 82
;
title "Sampled Defect Rates";
proc print data=samples;
run;
Output 11.2.1: Measured Defect Rates
proc expand data=samples out=monthly to=month;
id date;
convert defects / observed=(beginning,average);
run;
title "Estimated Monthly Average Defect Rates";
proc print data=monthly;
run;
The results are printed in Output 11.2.2.
Output 11.2.2: Monthly Average Estimates
|
proc expand data=samples out=daily to=day;
id date;
convert defects = interpol;
run;
data daily;
merge daily samples;
by date;
run;
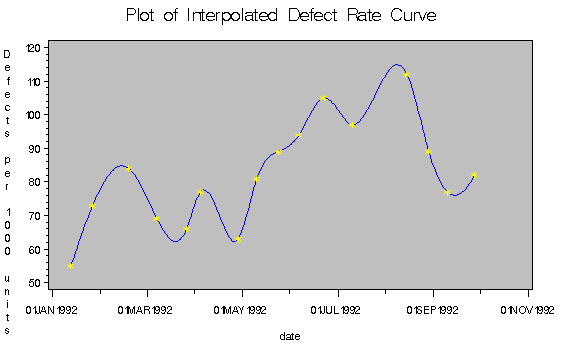
title "Plot of Interpolated Defect Rate Curve";
proc gplot data=daily;
axis2 label=(a=-90 r=90 );
symbol1 v=none i=join;
symbol2 v=star i=none;
plot interpol * date = 1 defects * date = 2 /
vaxis=axis2 overlay;
run;
quit;
The plot is shown in Output 11.2.3.
Output 11.2.3: Interpolated Defects Rate Curve
|
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.