Convergence Criteria
There are a number of measures that could be used as convergence or
stopping criteria. PROC MODEL computes five convergence measures
labeled R, S, PPC, RPC, and OBJECT.
When an estimation technique that iterates estimates of  is used
(that is, IT3SLS),
two convergence criteria are used. The termination values
can be specified with the CONVERGE=(p,s) option on the
FIT statement. If the second value, s, is not specified, it
defaults to p.
The criterion labeled S (given in the following)
controls the convergence of the
S matrix. When S is less than s, the S matrix
has converged.
The criterion labeled R is compared to the p value to test convergence
of the parameters.
is used
(that is, IT3SLS),
two convergence criteria are used. The termination values
can be specified with the CONVERGE=(p,s) option on the
FIT statement. If the second value, s, is not specified, it
defaults to p.
The criterion labeled S (given in the following)
controls the convergence of the
S matrix. When S is less than s, the S matrix
has converged.
The criterion labeled R is compared to the p value to test convergence
of the parameters.
The R convergence measure cannot be computed accurately in the special
case of singular residuals (when all the residuals are close to 0) or
in the case of a 0 objective value. When
either the trace of the S matrix
computed from the current residuals (trace(S)) or the objective value is
less than the value of the SINGULAR= option, convergence is assumed.
The various convergence measures are explained in the following:
- R
- is the primary convergence measure for the parameters.
It measures the degree to which the residuals are orthogonal to the
Jacobian columns, and it approaches 0 as the gradient of the
objective function becomes small.
R is defined as the square root of

where X is the Jacobian matrix and r is the residuals vector.
R is similar to the relative offset orthogonality convergence
criterion proposed by Bates and Watts (1981).
In the univariate case, the R measure has several equivalent
interpretations:
- the cosine of the angle between the residuals vector and the
column space of the Jacobian matrix.
When this cosine is 0, the residuals are orthogonal to the
partial derivatives of the predicted values with respect to the
parameters, and the gradient of the objective function is 0.
- the square root of the R2 for the current linear
pseudo-model in the residuals.
- a norm of the gradient of the objective function, where the norming
matrix is proportional to the current estimate of the covariance of the
parameter estimates. Thus, using R, convergence is judged when the
gradient becomes small in this norm.
- the prospective relative change in the objective function value
expected from the next GAUSS step, assuming that the
current linearization of the model is a good local approximation.
In the multivariate case, R is somewhat more complicated but is designed
to go to 0 as the gradient of the objective becomes small and can
still be given the previous interpretations for the aggregation of the
equations weighted by S-1.
- PPC
- is the prospective parameter change measure.
PPC measures the maximum relative change in the parameters implied by
the parameter-change vector computed for the next iteration.
At the kth iteration, PPC is the maximum over the parameters

where 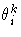 is the current value of the ith parameter and
is the current value of the ith parameter and
 is the prospective value of this parameter after
adding the change vector computed for the next iteration.
The parameter with the maximum prospective
relative change is printed with the value of PPC, unless the PPC is
nearly 0.
is the prospective value of this parameter after
adding the change vector computed for the next iteration.
The parameter with the maximum prospective
relative change is printed with the value of PPC, unless the PPC is
nearly 0.
- RPC
- is the retrospective parameter change measure.
RPC measures the maximum relative change in the parameters from the previous
iteration. At the kth iteration, RPC is the maximum over i of

where 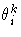 is the current value of the ith parameter and
is the current value of the ith parameter and
 is the previous value of this parameter.
The name of the parameter with the maximum retrospective
relative change is printed with the value of RPC, unless the RPC is nearly
0.
is the previous value of this parameter.
The name of the parameter with the maximum retrospective
relative change is printed with the value of RPC, unless the RPC is nearly
0.
- OBJECT
- measures the relative change in the objective
function value between iterations:

where Ok-1 is the value of the objective function (Ok)
from the previous iteration.
- S
- measures the relative change in the S matrix.
S is computed as the maximum over i, j of

where Sk-1 is the previous S matrix.
The S measure is relevant only for estimation methods that iterate the S matrix.
An example of the convergence criteria output is as follows:
|
| The MODEL Procedure |
| IT3SLS Estimation Summary |
| Minimization Summary |
| Parameters Estimated |
5 |
| Method |
Gauss |
| Iterations |
35 |
| Final Convergence Criteria |
| R |
0.000883 |
| PPC(d1) |
0.000644 |
| RPC(d1) |
0.000815 |
| Object |
0.00004 |
| Trace(S) |
3599.982 |
| Objective Value |
0.435683 |
| S |
0.000052 |
|
Figure 14.16: Convergence Criteria Output
This output indicates
the total number of iterations required by the Gauss minimization
for all the S matrices was 35.
The "Trace(S)" is the trace (the sum of the diagonal elements) of
the S matrix computed from the current residuals.
This row is labeled MSE if there is only one equation.
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.
![]() is used
(that is, IT3SLS),
two convergence criteria are used. The termination values
can be specified with the CONVERGE=(p,s) option on the
FIT statement. If the second value, s, is not specified, it
defaults to p.
The criterion labeled S (given in the following)
controls the convergence of the
S matrix. When S is less than s, the S matrix
has converged.
The criterion labeled R is compared to the p value to test convergence
of the parameters.
is used
(that is, IT3SLS),
two convergence criteria are used. The termination values
can be specified with the CONVERGE=(p,s) option on the
FIT statement. If the second value, s, is not specified, it
defaults to p.
The criterion labeled S (given in the following)
controls the convergence of the
S matrix. When S is less than s, the S matrix
has converged.
The criterion labeled R is compared to the p value to test convergence
of the parameters.




