Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The MODEL Procedure |
The following is a simplified reaction scheme for the competitive inhibitors with recombinant human renin (Morelock et al. 1995).
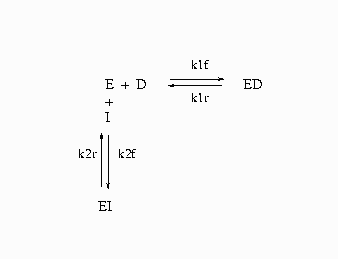
|
Figure 14.82: Competitive Inhibition of Recombinant Human Renin
In Figure 14.82, E= enzyme, D= probe, and I= inhibitor.
The differential equations describing this reaction scheme are
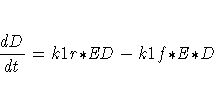
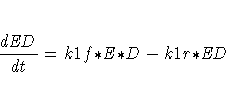
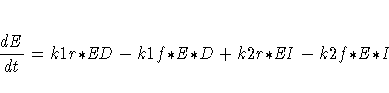
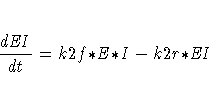
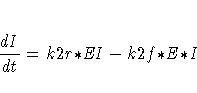
For this system, the initial values for the concentrations are derived from equilibrium considerations (as a function of parameters) or are provided as known values.
The experiment used to collect the data was carried out in two ways; pre-incubation (type='disassoc') and no pre-incubation (type='assoc'). The data also contain repeated measurements. The data contain values for fluorescence F, which is a function of concentration. Since there are no direct data for the concentrations, all the differential equations are simulated dynamically.
The SAS statements used to fit this model are
proc model data=fit;
parameters qf = 2.1e8
qb = 4.0e9
k2f = 1.8e5
k2r = 2.1e-3
l = 0;
k1f = 6.85e6;
k1r = 3.43e-4;
/* Initial values for concentrations */
control dt 5.0e-7
et 5.0e-8
it 8.05e-6;
/* Association initial values --------------*/
if type = 'assoc' and time=0 then
do;
ed = 0;
/* solve quadratic equation ----------*/
a = 1;
b = -(&it+&et+(k2r/k2f));
c = &it*&et;
ei = (-b-(((b**2)-(4*a*c))**.5))/(2*a);
d = &dt-ed;
i = &it-ei;
e = &et-ed-ei;
end;
/* Disassociation initial values ----------*/
if type = 'disassoc' and time=0 then
do;
ei = 0;
a = 1;
b = -(&dt+&et+(&k1r/&k1f));
c = &dt*&et;
ed = (-b-(((b**2)-(4*a*c))**.5))/(2*a);
d = &dt-ed;
i = &it-ei;
e = &et-ed-ei;
end;
if time ne 0 then
do;
dert.d = k1r* ed - k1f *e *d;
dert.ed = k1f* e *d - k1r*ed;
dert.e = k1r* ed - k1f* e * d + k2r * ei - k2f * e *i;
dert.ei = k2f* e *i - k2r * ei;
dert.i = k2r * ei - k2f* e *i;
end;
/* L - offset between curves */
if type = 'disassoc' then
F = (qf*(d-ed)) + (qb*ed) -L;
else
F = (qf*(d-ed)) + (qb*ed);
Fit F / method=marquardt;
run;
This estimation requires the repeated simulation of a system of 42 differential equations (5 base differential equations and 36 differential equations to compute the partials with respect to the parameters).
The results of the estimation are shown in Output 14.10.1.
Output 14.10.1: Kinetics Estimation
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.