Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The SPECTRA Procedure |
This example shows cross-spectral analysis for two variables X and Y using simulated data. X is generated by an AR(1) process; Y is generated as white noise plus an input from X lagged 2 periods. All output options are specified on the PROC SPECTRA statement. PROC CONTENTS shows the contents of the OUT= data set.
data a;
xl = 0; xll = 0;
do i = - 10 to 100;
x = .4 * xl + rannor(123);
y = .5 * xll + rannor(123);
if i > 0 then output;
xll = xl; xl = x;
end;
run;
proc spectra data=a out=b cross coef a k p ph s;
var x y;
weights 1 1.5 2 4 8 9 8 4 2 1.5 1;
run;
proc contents data=b position;
run;
The PROC CONTENTS report for the output data set B is shown in Output 17.2.1.
Output 17.2.1: Contents of PROC SPECTRA OUT= Data Set
symbol1 i=splines v=dot;
proc gplot data=b;
plot a_01_02 * freq;
run;
proc gplot data=b;
plot a_01_02 * period;
where period < 25;
run;
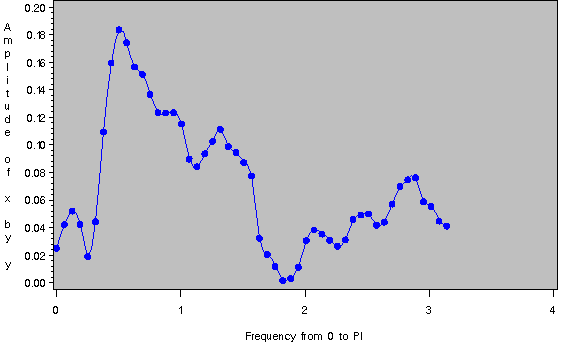
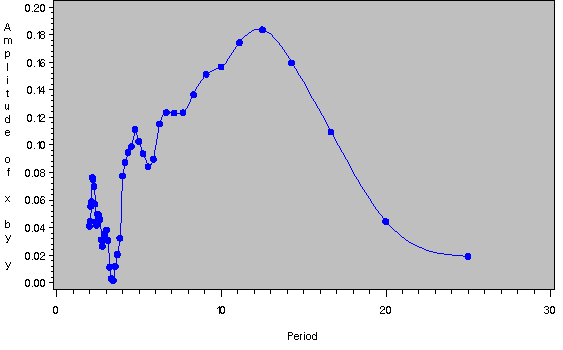
The plot of the amplitude of the cross-spectrum estimate against frequency is shown in Output 17.2.2. The plot of the cross-spectrum amplitude against period for periods less than 25 observations is shown in Output 17.2.3.
Output 17.2.2: Plot of Cross-Spectrum Amplitude by Frequency
|
|
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.