Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The STATESPACE Procedure |
The model is zt+1 = Fzt+Get+1,
where et is a sequence of independent multivariate
normal innovations with mean vector 0 and variance
![]() .The observed sequence, xt, composes the first r
components of zt and, thus,
xt = Hzt,
where H is the r ×s matrix
[Ir 0].
.The observed sequence, xt, composes the first r
components of zt and, thus,
xt = Hzt,
where H is the r ×s matrix
[Ir 0].
Let E be the r ×n matrix of innovations:
![E = [\matrix{e_{1} & { ... } & e_{n} }]](images/staeq51.gif)
If the number of observations, n, is reasonably large, the log likelihood, L, can be approximated up to an additive constant as follows:
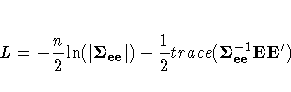
The elements of ![]() are taken as free parameters
and are estimated as follows:
are taken as free parameters
and are estimated as follows:
Replacing ![]() by S0
in the likelihood equation,
the log likelihood, up to an additive constant, is
by S0
in the likelihood equation,
the log likelihood, up to an additive constant, is
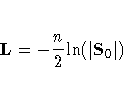
Letting B be the backshift operator, the formal relation between xt and et is
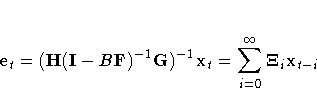
Letting Ci be the ith lagged sample covariance of xt, and neglecting end effects, the matrix S0 is
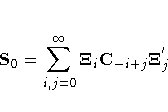
For the computation of S0,
the infinite sum is truncated at the value of the KLAG= option.
The value of the KLAG= option should be large enough that
the sequence ![]() is approximately 0 beyond that point.
is approximately 0 beyond that point.
Let ![]() be the vector of free parameters in the
F and G matrices.
The derivative of the log likelihood
with respect to the parameter
be the vector of free parameters in the
F and G matrices.
The derivative of the log likelihood
with respect to the parameter ![]() is
is
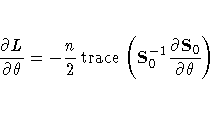
The second derivative is
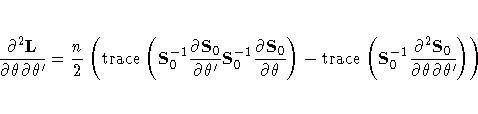
Near the maximum, the first term is unimportant and the second term can be approximated to give the following second derivative approximation:
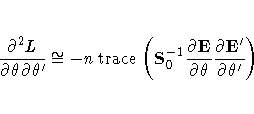
The first derivative matrix and this second derivative matrix approximation
are computed from the sample covariance matrix C0
and the truncated sequence ![]() .The approximate likelihood function is maximized by a
modified Newton-Raphson algorithm employing these derivative matrices.
.The approximate likelihood function is maximized by a
modified Newton-Raphson algorithm employing these derivative matrices.
The matrix S0 is used as the estimate of the innovation
covariance matrix, ![]() .The negative of the inverse of the second derivative matrix at the maximum
is used as an approximate covariance matrix for the parameter estimates.
The standard errors of the parameter estimates printed in the
parameter estimates tables are taken from the diagonal of this
covariance matrix.
The parameter covariance matrix is printed when the COVB option is specified.
.The negative of the inverse of the second derivative matrix at the maximum
is used as an approximate covariance matrix for the parameter estimates.
The standard errors of the parameter estimates printed in the
parameter estimates tables are taken from the diagonal of this
covariance matrix.
The parameter covariance matrix is printed when the COVB option is specified.
If the data are nearly nonstationary, a better
estimate of ![]() and the other parameters can
sometimes be obtained by specifying the RESIDEST option.
The RESIDEST option estimates the parameters using conditional least squares
instead of maximum likelihood.
and the other parameters can
sometimes be obtained by specifying the RESIDEST option.
The RESIDEST option estimates the parameters using conditional least squares
instead of maximum likelihood.
The residuals are computed using the state space equation and the
sample mean values of the variables in the model as start-up values.
The estimate of S0 is then computed using the residuals
from the ith observation on, where i is the maximum number
of times any variable occurs in the state vector.
A multivariate Gauss-Marquardt algorithm is used to
minimize ![]() .Refer to Harvey (1981a) for a further description of this method.
.Refer to Harvey (1981a) for a further description of this method.
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.