Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| Fit Analyses |
A standard measure of goodness of fit is the mean residual sum of squares
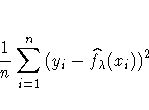
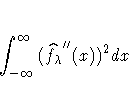
A single criterion that combines the two criteria is then given by
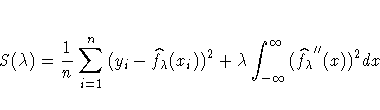
The estimator that results from minimizing S(![]() )is called the smoothing spline estimator.
This estimator fits a cubic polynomial
in each interval between points.
At each point xi, the curve and its
first two derivatives are continuous (Reinsch 1967).
The smoothing parameter
)is called the smoothing spline estimator.
This estimator fits a cubic polynomial
in each interval between points.
At each point xi, the curve and its
first two derivatives are continuous (Reinsch 1967).
The smoothing parameter ![]() controls the amount of
smoothing; that is, it controls the trade-off between the
goodness of fit to the data and the smoothness of the fit.
You select a smoothing parameter
controls the amount of
smoothing; that is, it controls the trade-off between the
goodness of fit to the data and the smoothness of the fit.
You select a smoothing parameter ![]() by
specifying a constant c in the formula
by
specifying a constant c in the formula
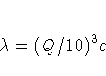
After choosing Curves:Spline, you specify a smoothing parameter selection method in the Spline Fit dialog.
The default Method:GCV uses a c value that
minimizes the generalized cross validation mean
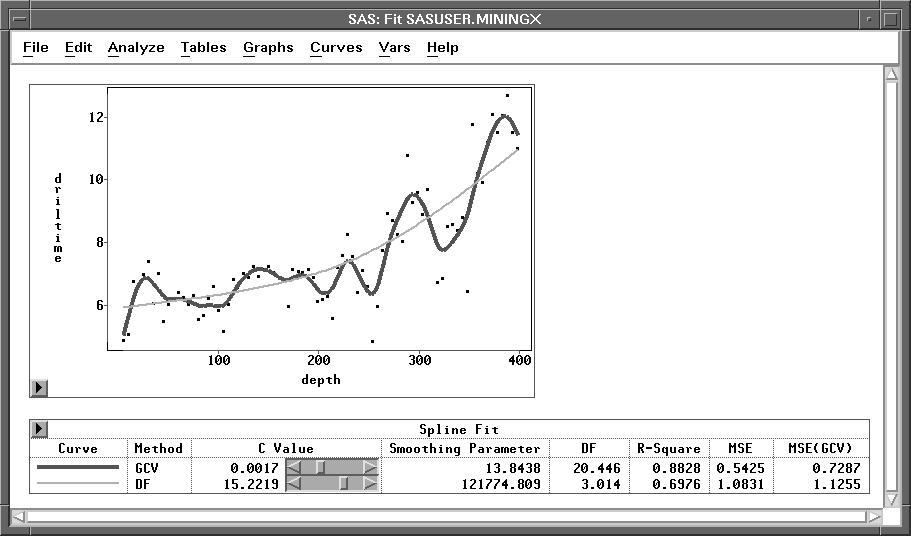
squared error ![]() .Figure 39.41 displays smoothing spline estimates
with c values of 0.0017 (the GCV value) and 15.2219 (DF=3).
Use the slider in the table to change
the c value of the spline fit.
.Figure 39.41 displays smoothing spline estimates
with c values of 0.0017 (the GCV value) and 15.2219 (DF=3).
Use the slider in the table to change
the c value of the spline fit.
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.