IS-IS
The IS-IS routing protocol is a link state protocol for interior routing.
It is an ISO standard and is completely defined in [ISO/IEC-10589].
The ES-IS neighbor greeting protocol is used in conjunction with IS-IS.
For its hierarchical routing, IS-IS divides the network into nonoverlapping
IS-IS areas and its routers are categorized as Level 1 or Level 2 routers,
or both.
Level 1 routers are responsible for routing packets between LANs
within an IS-IS area, and Level 2 routers forward packets between IS-IS areas.
A sample IS-IS topology is depicted in Figure A.7.
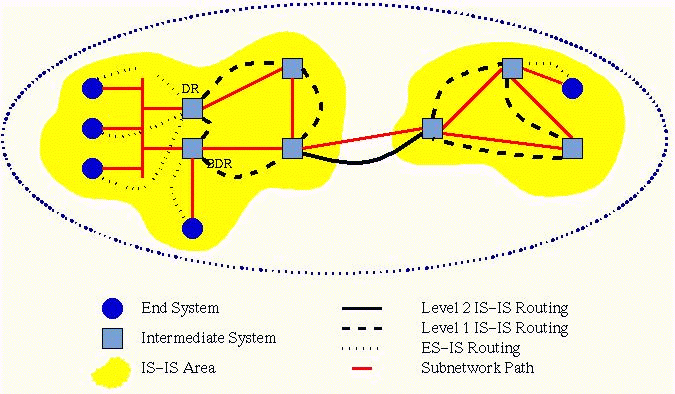
Figure A.7: Sample IS-IS Topology
In the IS-IS routing protocol, Level 1 routers transmit Level 1
hello packets to the other Level 1 routers on the LANs to which they
are connected.
Level 2 routers operate in a similar manner.
(Note that a LAN may actually be a point-to-point connection between
two routers.)
The routers collect and process all of their neighbor routers
hello packets and populate a local cache with the state of all its
router links.
Each router (or DR for a LAN) periodically floods its link state
information to all other routers at its level in a Link State packet.
The routers use all the link state information to create a
graph of the network.
From this graph, the router is able to determine the "best"
path for forwarding packets it receives; that is,
the router creates a table (or forwarding database) stating which
port to use to transmit packets towards their destination.
The basic algorithm used for route calculation is the
shortest path first algorithm invented by Dijkstra and described
in [Aho 1983].
Routers periodically recalculate their routing tables to reflect
any new link state information.
A Level 1 router recognizes the fact that a data packet is destined
for another IS-IS area and forwards the packet to a Level 2 router
for inter-Area routing.
The netWorks simulation of the IS-IS routing protocol does
not support Level 2 routing at this time.
The IS-IS protocol provides a number of configurable parameters that
can be tuned for your particular network model.
The IS-IS control panel for a Router model, shown in
Figure A.8, displays the protocol parameters you can change in the
netWorks version of IS-IS.
You should be fairly familiar with the internals of the IS-IS protocol
before you edit these fields.
Note that units for the Timing Intervals are milliseconds.
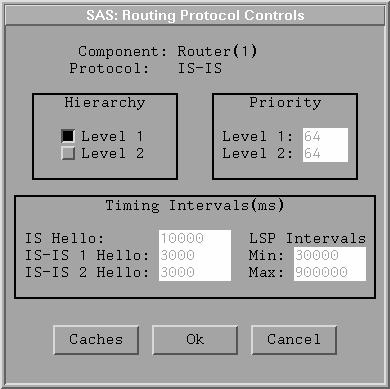
Figure A.8: Sample IS-IS Protocol Controls
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.

