Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| QQPLOT Statement |
| See CAPQQ1 in the SAS/QC Sample Library |
Measurements of the distance between two holes cut into 50 steel sheets are saved as values of the variable DISTANCE in the following data set:
data sheets;
input distance @@;
label distance='Hole Distance in cm';
datalines;
9.80 10.20 10.27 9.70 9.76
10.11 10.24 10.20 10.24 9.63
9.99 9.78 10.10 10.21 10.00
9.96 9.79 10.08 9.79 10.06
10.10 9.95 9.84 10.11 9.93
10.56 10.47 9.42 10.44 10.16
10.11 10.36 9.94 9.77 9.36
9.89 9.62 10.05 9.72 9.82
9.99 10.16 10.58 10.70 9.54
10.31 10.07 10.33 9.98 10.15
;
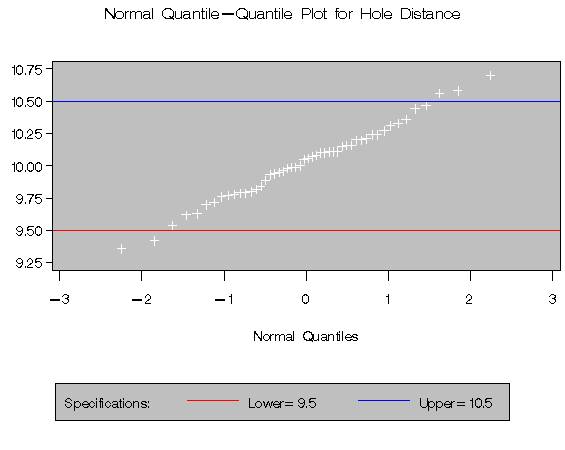
The cutting process is in control, and you decide to check whether the process distribution is normal. The following statements create a Q-Q plot for DISTANCE, shown in Figure 10.1, with lower and upper specification lines at 9.5 cm and 10.5 cm:*
title 'Normal Quantile-Quantile Plot for Hole Distance';
legend1 frame cframe=ligr cborder=black position=center;
proc capability data=sheets noprint;
spec lsl=9.5 clsl=red
usl=10.5 cusl=blue;
qqplot distance / cframe = ligr
legend = legend1;
run;
The plot compares the ordered values of DISTANCE with quantiles of the normal distribution. The linearity of the point pattern indicates that the measurements are normally distributed. Note that a normal Q-Q plot is created by default. If you specify the LINEPRINTER option in the PROC CAPABILITY statement, the plot is created using a line printer, as shown in Figure 10.2. The specification lines are requested with the LSL= and USL= options in the SPEC statement.
|
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.