Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The NLMIXED Procedure |
| Option | Description |
| Basic Options | |
| DATA= | input data set |
| METHOD= | integration method |
| Displayed Output Specifications | |
| START | gradient at starting values |
| HESS | Hessian matrix |
| ITDETAILS | iteration details |
| CORR | correlation matrix |
| COV | covariance matrix |
| ECORR | corr matrix of additional estimates |
| ECOV | cov matrix of additional estimates |
| EDER | derivatives of additional estimates |
| ALPHA= | alpha for confidence limits |
| DF= | degrees of freedom for p values and confidence limits |
| Debugging Output | |
| LIST | model program, variables |
| LISTCODE | compiled model program |
| LISTDEP | model dependency listing |
| LISTDER | model derivative |
| XREF | model cross reference |
| FLOW | model execution messages |
| TRACE | detailed model execution messages |
| Quadrature Options | |
| NOAD | no adaptive centering |
| NOADSCALE | no adaptive scaling |
| OUTQ= | output data set |
| QFAC= | search factor |
| QMAX= | maximum points |
| QPOINTS= | number of points |
| QSCALEFAC= | scale factor |
| QTOL= | tolerance |
| Empirical Bayes Options | |
| EBSTEPS= | number of Newton steps |
| EBSUBSTEPS= | number of substeps |
| EBSSFRAC= | step-shortening fraction |
| EBSSTOL= | step-shortening tolerance |
| EBTOL= | convergence tolerance |
| EBOPT | comprehensive optimization |
| EBZSTART | zero starting values |
| Optimization Specifications | |
| TECHNIQUE= | minimization technique |
| UPDATE= | update technique |
| LINESEARCH= | line-search method |
| LSPRECISION= | line-search precision |
| HESCAL= | type of Hessian scaling |
| INHESSIAN= | start for approximated Hessian |
| RESTART= | iteration number for update restart |
| OPTCHECK[=] | check optimality in neighborhood |
| Derivatives Specifications | |
| FD[=] | finite-difference derivatives |
| FDHESSIAN[=] | finite-difference second derivatives |
| DIAHES | use only diagonal of Hessian |
| Constraint Specifications | |
| LCEPSILON= | range for active constraints |
| LCDEACT= | LM tolerance for deactivating |
| LCSINGULAR= | tolerance for dependent constraints |
| Termination Criteria Specifications | |
| MAXFUNC= | maximum number of function calls |
| MAXITER= | maximum number of iterations |
| MINITER= | minimum number of iterations |
| MAXTIME= | upper limit seconds of CPU time |
| ABSCONV= | absolute function convergence criterion |
| ABSFCONV= | absolute function convergence criterion |
| ABSGCONV= | absolute gradient convergence criterion |
| ABSXCONV= | absolute parameter convergence criterion |
| FCONV= | relative function convergence criterion |
| FCONV2= | relative function convergence criterion |
| GCONV= | relative gradient convergence criterion |
| XCONV= | relative parameter convergence criterion |
| FDIGITS= | number accurate digits in objective function |
| FSIZE= | used in FCONV, GCONV criterion |
| XSIZE= | used in XCONV criterion |
| Step Length Specifications | |
| DAMPSTEP[=] | damped steps in line search |
| MAXSTEP= | maximum trust-region radius |
| INSTEP= | initial trust-region radius |
| Singularity Tolerances | |
| SINGCHOL= | tolerance for Cholesky roots |
| SINGHESS= | tolerance for Hessian |
| SINGSWEEP= | tolerance for sweep |
| SINGVAR= | tolerance for variances |
| Covariance Matrix Tolerances | |
| ASINGULAR= | absolute singularity for inertia |
| MSINGULAR= | relative M singularity for inertia |
| VSINGULAR= | relative V singularity for inertia |
| G4= | threshold for Moore-Penrose inverse |
| COVSING= | tolerance for singular COV matrix |
| CFACTOR= | multiplication factor for COV matrix |

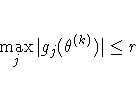
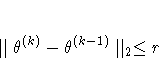
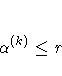
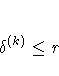

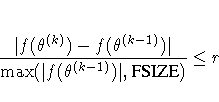
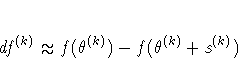

![\sqrt{ {1 \over n+1} \sum_l [ f(\theta_l^{(k)}) -
\overline{f}(\theta^{(k)}) ]^2 } \leq r](images/nlmeq31.gif)
![{ g(\theta^{(k)})^T [H^{(k)}]^{-1} g(\theta^{(k)}) \over
\max(| f(\theta^{(k)})|,{FSIZE}) } \leq r](images/nlmeq34.gif)
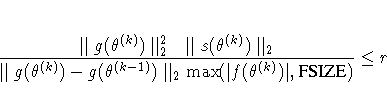

![d_i^{(k+1)} = \max [ d_i^{(k)},\sqrt{\max(| H^{(k)}_{i,i}|,
\epsilon)} ]](images/nlmeq38.gif)
![d_i^{(k+1)} = \max [ 0.6 * d_i^{(k)},
\sqrt{\max(| H^{(k)}_{i,i}|,\epsilon)} ]](images/nlmeq39.gif)

| TECH= | UPDATE= | LSP default |
| QUANEW | DBFGS, BFGS | r = 0.4 |
| QUANEW | DDFP, DFP | r = 0.06 |
| CONGRA | all | r = 0.1 |
| NEWRAP | no update | r = 0.9 |
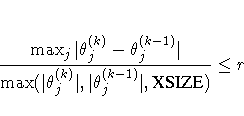
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.