Reading for Today's Lecture: Chapter 3
Goals of Today's Lecture:
Conditional Expectations
Example:
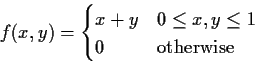
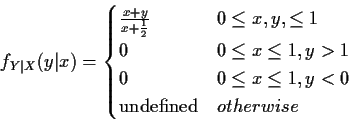
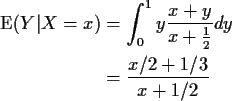
Computing expectations by conditioning:
Notation:
![]() is the function of X you get by
working out
is the function of X you get by
working out
![]() ,
getting a formula in x and replacing
x by X. This makes
,
getting a formula in x and replacing
x by X. This makes
![]() a random variable.
a random variable.
Properties:
1:
![]() .
.
2: If Y and X are independent then
3:
![]() .
.
4:
![]() (compute average
holding X fixed first, then average over X).
(compute average
holding X fixed first, then average over X).
In example:
Application to last names problem.
Put
![]()
![\begin{align*}{\rm E}(Z_n) & = {\rm E}\left[{\rm E}(Z_n\vert X)\right]
\\
& = {...
...Z_{n-2})
\\
& \quad \vdots
\\
& = m^{n-1}{\rm E}(Z_1)
\\
& = m^n
\end{align*}](img14.gif)
For m < 1 expect exponential decay. For m>1 exponential growth (if not extinction).