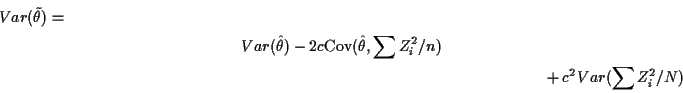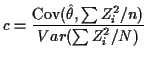Given random variables
![]() whose joint density
whose joint density ![]() (or distribution)
is specified and a statistic
(or distribution)
is specified and a statistic
![]() whose distribution you want to know. To compute
something like
whose distribution you want to know. To compute
something like ![]() :
:
Notice accuracy inversely proportional to ![]() .
There are a number of tricks to make the method more accurate
(but they only change the constant of proportionality - the SE is still
inversely proportional to the square root of the sample size).
.
There are a number of tricks to make the method more accurate
(but they only change the constant of proportionality - the SE is still
inversely proportional to the square root of the sample size).
Transformation
Most computer languages have a facility for generating pseudo uniform
random numbers, that is, variables ![]() which have (approximately of course) a
Uniform
which have (approximately of course) a
Uniform![]() distribution. Other distributions are generated by
transformation:
distribution. Other distributions are generated by
transformation:
Exponential: ![]() has an exponential distribution:
has an exponential distribution:
General technique: inverse probability integral transform.
If ![]() is to have cdf
is to have cdf ![]() :
:
Generate
![]() .
.
Take
![]() :
:
Example: ![]() exponential.
exponential.
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
Compare to previous method. (Use ![]() instead of
instead of
![]() .)
.)
Normal: ![]() (common notation
for standard normal cdf).
(common notation
for standard normal cdf).
No closed form for ![]() .
.
One way: use numerical algorithm to compute ![]() .
.
Alternative: Box Müller
Generate ![]() two independent Uniform[0,1] variables.
two independent Uniform[0,1] variables.
Define
Exercise: (use change of variables) ![]() and
and ![]() are independent
are independent
![]() variables.
variables.
Acceptance Rejection
Suppose: can't calculate ![]() but know
but know ![]() .
.
Find density ![]() and constant
and constant
![]() such that
such that
Algorithm:
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
Recently popular tactic, particularly for generating multivariate observations.
Theorem Suppose
![]() is an
(ergodic) Markov chain with stationary transitions and the stationary
initial distribution of
is an
(ergodic) Markov chain with stationary transitions and the stationary
initial distribution of ![]() has density
has density ![]() . Then starting the
chain with any initial distribution
. Then starting the
chain with any initial distribution
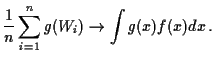
Estimate things like
![]() by computing the fraction of the
by computing the fraction of the ![]() which land in
which land in
![]() .
.
Many versions of this technique including Gibbs Sampling and Metropolis-Hastings algorithm.
Technique invented in 1950s: Metropolis et al.
One of the authors was Edward Teller ``father of the hydrogen bomb''.
Importance Sampling
If you want to compute
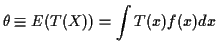
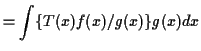 |
||
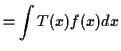 |
||
Variance reduction
Consider the problem of estimating the distribution of the sample mean for a Cauchy random variable. The Cauchy density is
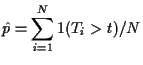
We can improve this estimate by remembering that ![]() also
has Cauchy distribution. Take
also
has Cauchy distribution. Take ![]() . Remember that
. Remember that ![]() has
the same distribution as
has
the same distribution as ![]() . Then we try (for
. Then we try (for ![]() )
)
![$\displaystyle \tilde p = [\sum_{i=1}^N 1(T_i > t) + \sum_{i=1}^N 1(S_i > t) ]/(2N)
$](img90.gif)

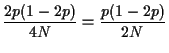
Regression estimates
Suppose we want to compute