Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The AUTOREG Procedure |
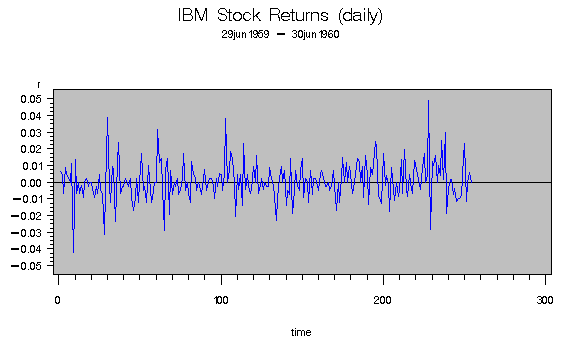
Stock returns show a tendency for small changes to be followed by small changes while large changes are followed by large changes. The plot of daily price changes of the IBM common stock (Box and Jenkins 1976, p 527) are shown in Output 8.6.1. The time series look serially uncorrelated, but the plot makes us skeptical of their independence.
With a DATA step, the stock (capital) returns are computed from the closing prices. To forecast the conditional variance, an additional 46 observations with missing values are generated.
title 'IBM Stock Returns (daily)';
title2 '29jun1959 - 30jun1960';
data ibm;
infile datalines eof=last;
input x @@;
r = dif( log( x ) );
time = _n_-1;
output;
return;
last:
do i = 1 to 46;
r = .;
time + 1;
output;
end;
return;
datalines;
;
proc gplot data=ibm;
plot r*time / vref=0;
symbol1 i=join v=none;
run;
Output 8.6.1: IBM Stock Returns: Daily
|


proc autoreg data=ibm maxit=50;
model r = / noint garch=(q=2);
output out=a cev=v;
run;
The parameter estimates for
![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() are 0.00011, 0.04136, and
0.06976, respectively. The normality test indicates that
the conditional normal distribution
may not fully explain the leptokurtosis in the
stock returns (Bollerslev 1987).
are 0.00011, 0.04136, and
0.06976, respectively. The normality test indicates that
the conditional normal distribution
may not fully explain the leptokurtosis in the
stock returns (Bollerslev 1987).
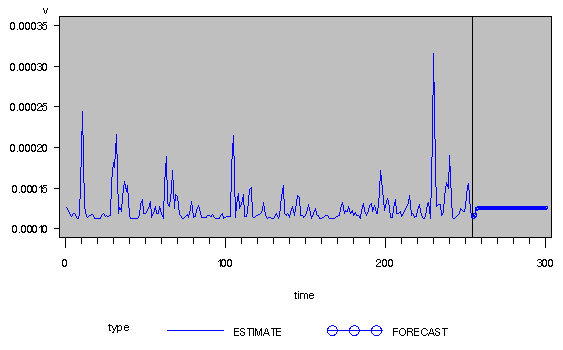
The ARCH model estimates are shown in Output 8.6.2, and conditional variances are also shown in Output 8.6.3.
Output 8.6.2: ARCH(2) Estimation ResultsOutput 8.6.3: Conditional Variance for IBM Stock Prices
|
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.