Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| Nonlinear Optimization Examples |
| Index | Description |
| 1 | specifies minimization, maximization, or the number of least-squares functions |
| 2 | specifies the amount of printed output |
| 3 | NLPDD, NLPLM, NLPNRA, NLPNRR, NLPTR: specifies the scaling of the Hessian matrix (HESCAL) |
| 4 | NLPCG, NLPDD, NLPHQN, NLPQN: specifies the update technique (UPDATE) |
| 5 | NLPCG, NLPHQN, NLPNRA, NLPQN (with no nonlinear constraints): specifies the line-search technique (LIS) |
| 6 | NLPHQN: specifies version of hybrid algorithm (VERSION) |
| NLPQN with nonlinear constraints: specifies
version of | |
| 7 | NLPDD, NLPHQN, NLPQN: specifies initial Hessian matrix (INHESSIAN) |
| 8 | Finite Difference Derivatives: specifies type of differences and how to compute the difference interval |
| 9 | NLPNRA: specifies the number of rows returned by the sparse Hessian module |
| 10 | NLPNMS, NLPQN: specifies the total number of constraints returned by the "nlc" module |
| 11 | NLPNMS, NLPQN: specifies the number of equality constraints returned by the "nlc" module |
The following list contains detailed explanations of the elements of the options vector:
| Value of opt[2] | Printed Output |
| 0 | No printed output is produced. This is the default. |
| 1 | The summaries for optimization start and termination are produced, as well as the iteration history. |
| 2 | The initial and final parameter estimates are also printed. |
| 3 | The values of the termination criteria and other control parameters are also printed. |
| 4 | The parameter vector, x, is also printed after each iteration. |
| 5 | The gradient vector, g, is also printed after each iteration. |
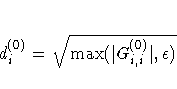
| Value of opt[3] | Scaling Update |
| 0 | No scaling is done. |
| 1 | Mor |
| 2 | Dennis, Gay, and Welsch (1981) scaling update:
|
| 3 | di is reset in each iteration:
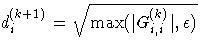 |
For the NLPDD, NLPNRA, NLPNRR, and NLPTR subroutines, the default is opt[3]=0; for the NLPLM subroutine, the default is opt[3]=1.
| Value of opt[4] | Update Method for NLPCG |
| 1 | automatic restart method of Powell (1977) and Beale (1972). This is the default. |
| 2 | Fletcher-Reeves update (Fletcher 1987) |
| 3 | Polak-Ribiere update (Fletcher 1987) |
| 4 | Conjugate-descent update of Fletcher (1987) |
For the unconstrained or linearly constrained NLPQN subroutine, the following update techniques are available.
| Value of opt[4] | Update Method for NLPQN |
| 1 | dual Broyden, Fletcher, Goldfarb, and Shanno (DBFGS) update of the Cholesky factor of the Hessian matrix. This is the default. |
| 2 | dual Davidon, Fletcher, and Powell (DDFP) update of the Cholesky factor of the Hessian matrix |
| 3 | original Broyden, Fletcher, Goldfarb, and Shanno (BFGS) update of the inverse Hessian matrix |
| 4 | original Davidon, Fletcher, and Powell (DFP) update of the inverse Hessian matrix |
For the NLPQN subroutine used with the "nlc" module and for the NLPDD and NLPHQN subroutines, only the first two update techniques in the second table are available.
| Value of opt[5] | Line-Search Method |
| 1 | This method needs the same number of function and gradient calls for cubic interpolation and cubic extrapolation; it is similar to a method used by the Harwell subroutine library. |
| 2 | This method needs more function than gradient calls for quadratic and cubic interpolation and cubic extrapolation; it is implemented as shown in Fletcher (1987) and can be modified to exact line search with the par[6] argument (see the "Control Parameters Vector" section). This is the default for the NLPCG, NLPNRA, and NLPQN subroutines. |
| 3 | This method needs the same number of function and gradient calls for cubic interpolation and cubic extrapolation; it is implemented as shown in Fletcher (1987) and can be modified to exact line search with the par[6] argument. |
| 4 | This method needs the same number of function and gradient calls for stepwise extrapolation and cubic interpolation. |
| 5 | This method is a modified version of the opt[5]=4 method. |
| 6 | This method is the golden section line search of Polak (1971), which uses only function values for linear approximation. |
| 7 | This method is the bisection line search of Polak (1971), which uses only function values for linear approximation. |
| 8 | This method is the Armijo line-search technique of Polak (1971), which uses only function values for linear approximation. |
For the NLPHQN least-squares subroutine, the default
is a special line-search method that is based on an
algorithm developed by Lindstr![]() m and Wedin (1984).
Although it needs more memory, this method sometimes
works better with large least-squares problems.
m and Wedin (1984).
Although it needs more memory, this method sometimes
works better with large least-squares problems.
In the NLPHQN subroutine, it defines the criterion for the decision of the hybrid algorithm to step in a Gauss-Newton or a quasi-Newton search direction. You can specify one of the three criteria that correspond to the methods of Fletcher and Xu (1987). The methods are HY1 (opt[6]=1), HY2 (opt[6]=2), and HY3 (opt[6]=2), and the default is HY2.
In the NLPQN subroutine with nonlinear constraints,
it defines the version of the algorithm used to
update the vector ![]() of the Lagrange multipliers.
The default is opt[6]=2, which
specifies the approach of Powell (1982a,b).
You can specify the approach of
Powell (1978b) with opt[6]=1.
of the Lagrange multipliers.
The default is opt[6]=2, which
specifies the approach of Powell (1982a,b).
You can specify the approach of
Powell (1978b) with opt[6]=1.
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.