Canonical Discriminant Analysis
You can generate tables of output from canonical discriminant analyses
by setting options in the Canonical Discriminant Options dialog
shown in Figure 40.10
or from the Tables menu shown in
Figure 40.11. Select Canonical Discrimination from the
Tables menu to display the canonical discriminant
analysis dialog shown in Figure 40.31.
Figure 40.31: Canonical Discriminant Analysis Dialog
The Canonical Correlations table,
as shown in Figure 40.32,
contains the following:
- CanCorr, the canonical correlations, which are always nonnegative
- Adj. CanCorr, the adjusted canonical correlations,
which are asymptotically less biased than the raw correlations
and may be
negative. The adjusted canonical correlations may not be computable and
are displayed as missing values if two canonical correlations are nearly
equal or if some are close to zero. A missing value is also displayed if
an adjusted canonical correlation is larger than a previous adjusted
canonical correlation.
- Approx Std. Error, the approximate standard
errors of the canonical correlations
- CanRsq, the squared canonical correlations
- Eigenvalues,
eigenvalues of the matrix E-1 H,
where E is the matrix of the within-class
sums of squares and crossproducts and H is the matrix of
the between-class sums of squares and crossproducts.
These eigenvalues are equal to CanRsq/(1-CanRsq),
where CanRsq is the corresponding squared canonical correlation.
Also displayed for each eigenvalue is the difference from
the next eigenvalue, the proportion of the sum of the eigenvalues,
and the cumulative proportion.
- Test for H0: CanCorrj=0, j>=k,
the likelihood ratio for the hypothesis that the current canonical
correlation and all smaller ones are zero in the population
- Approx F based on Rao's approximation to the distribution of the
likelihood ratio
- Num DF and Den DF (numerator and denominator
degrees of freedom) and
Pr > F (probability level) associated
with the F statistic
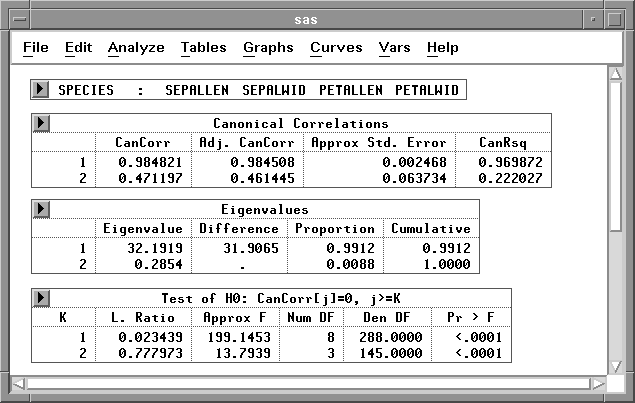
Figure 40.32: Canonical Correlations Tables
The Correlations (Structure) table includes the correlations
between the input X variables and the canonical variables.
The scoring coefficients are the coefficients
of the X variables that are used to compute
canonical variable scores.
The Std Scoring Coefs table includes the scoring coefficients
of the standardized X variables, and the Raw Scoring Coefs
table includes the scoring coefficients
of the centered X variables.
Figure 40.33 shows tables of
correlations
between the X variables and the first two canonical variables,
and the scoring coefficients of the standardized X variables.
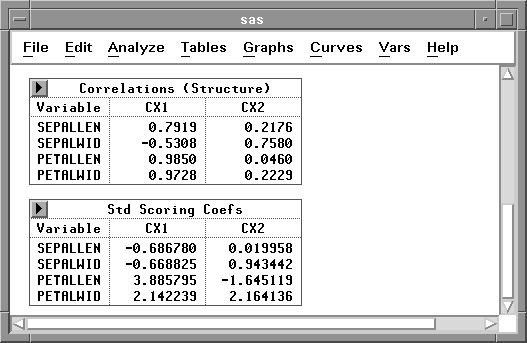
Figure 40.33: Correlations and Scoring Coefficients Tables
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.


