Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| Introduction to Clustering Procedures |
To see how various clustering methods differ, you must examine a more difficult problem than that of the previous example.
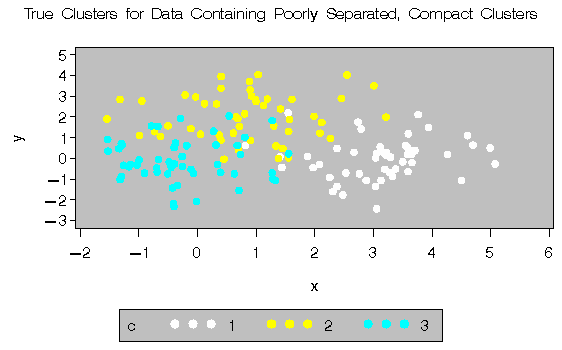
The following data set is similar to the first except that the three clusters are much closer together. This example demonstrates the use of PROC FASTCLUS and five hierarchical methods available in PROC CLUSTER. To help you compare methods, this example plots true, generated clusters. Also included is a bubble plot of the density estimates obtained in conjunction with two-stage density linkage in PROC CLUSTER. The following SAS statements produce Figure 8.2:
data closer;
keep x y c;
n=50; scale=1;
mx=0; my=0; c=3; link generate;
mx=3; my=0; c=1; link generate;
mx=1; my=2; c=2; link generate;
stop;
generate:
do i=1 to n;
x=rannor(9)*scale+mx;
y=rannor(9)*scale+my;
output;
end;
return;
run;
title 'True Clusters for Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
proc gplot;
plot y*x=c/frame cframe=ligr
vaxis=axis1 haxis=axis2 legend=legend1;
run;
|
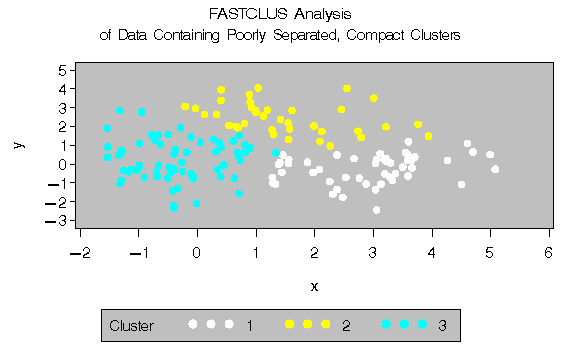
The following statements use the FASTCLUS procedure to find three clusters and the GPLOT procedure to plot the clusters. Since the GPLOT step is repeated several times in this example, it is contained in the PLOTCLUS macro. The following statements produce Figure 8.3.
%macro plotclus;
legend1 frame cframe=ligr cborder=black
position=center value=(justify=center);
axis1 minor=none label=(angle=90 rotate=0);
axis2 minor=none;
proc gplot;
plot y*x=cluster/frame cframe=ligr
vaxis=axis1 haxis=axis2 legend=legend1;
run;
%mend plotclus;
proc fastclus data=closer out=out maxc=3 noprint;
var x y;
title 'FASTCLUS Analysis';
title2 'of Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
%plotclus;
|
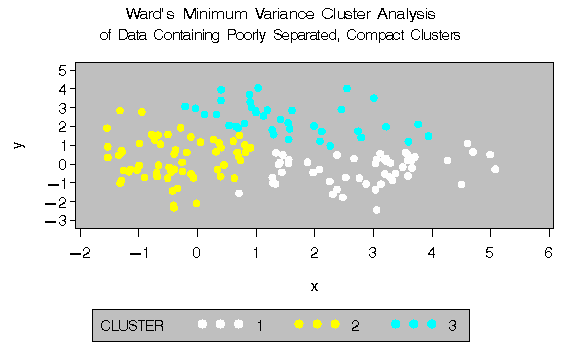
The following SAS statements produce Figure 8.4:
proc cluster data=closer outtree=tree method=ward noprint;
var x y;
run;
proc tree noprint out=out n=3;
copy x y;
title 'Ward''s Minimum Variance Cluster Analysis';
title2 'of Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
%plotclus;
|
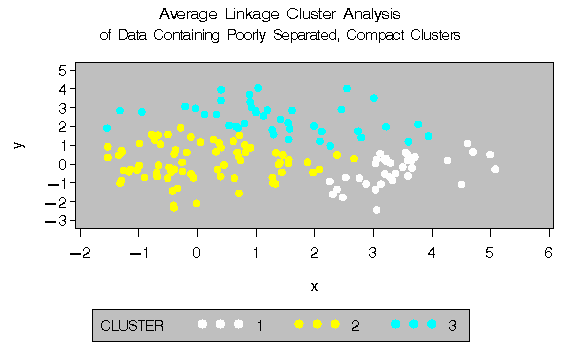
The following SAS statements produce Figure 8.5:
proc cluster data=closer outtree=tree method=average noprint;
var x y;
run;
proc tree noprint out=out n=3 dock=5;
copy x y;
title 'Average Linkage Cluster Analysis';
title2 'of Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
%plotclus;
|
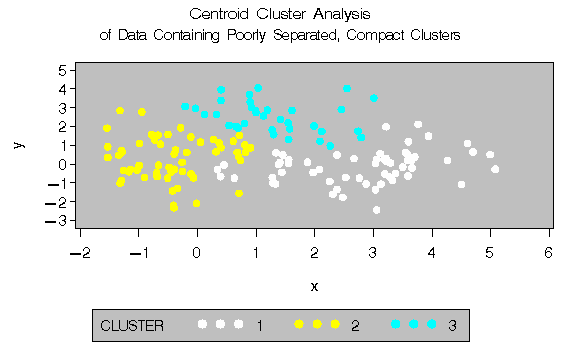
The following SAS statements produce Figure 8.6:
proc cluster data=closer outtree=tree
method=centroid noprint;
var x y;
run;
proc tree noprint out=out n=3 dock=5;
copy x y;
title 'Centroid Cluster Analysis';
title2 'of Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
%plotclus;
|
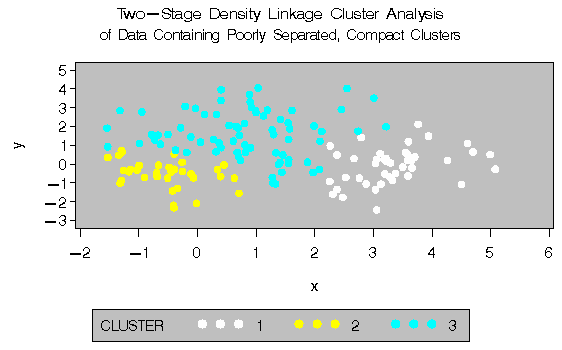
The following SAS statements produce Figure 8.7:
proc cluster data=closer outtree=tree
method=twostage k=10 noprint;
var x y;
run;
proc tree noprint out=out n=3;
copy x y _dens_;
title 'Two-Stage Density Linkage Cluster Analysis';
title2 'of Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
%plotclus;
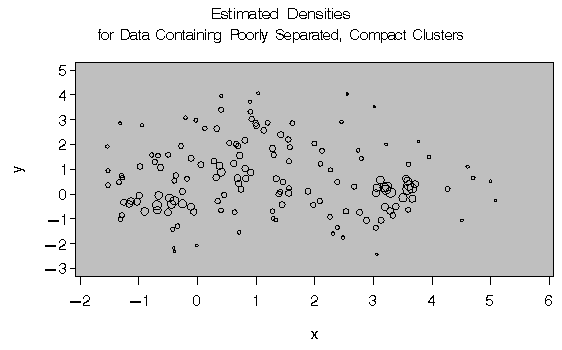
proc gplot;
bubble y*x=_dens_/frame cframe=ligr
vaxis=axis1 haxis=axis2;
title 'Estimated Densities';
title2 'for Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
|
|
In two-stage density linkage, each cluster is a region surrounding a local maximum of the estimated probability density function. If you think of the estimated density function as a landscape with mountains and valleys, each mountain is a cluster, and the boundaries between clusters are placed near the bottoms of the valleys.
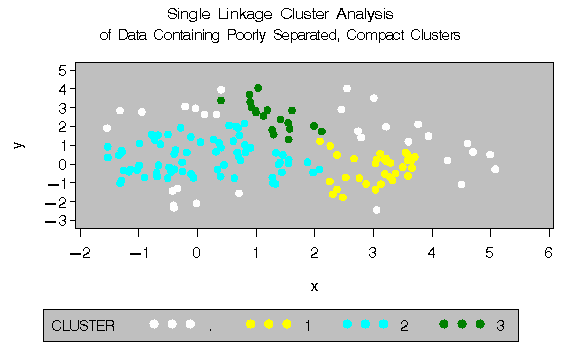
The following SAS statements produce Figure 8.8:
proc cluster data=closer outtree=tree
method=single noprint;
var x y;
run;
proc tree data=tree noprint out=out n=3 dock=5;
copy x y;
title 'Single Linkage Cluster Analysis';
title2 'of Data Containing Poorly Separated,
Compact Clusters';
run;
%plotclus;
|
The two least-squares methods, PROC FASTCLUS and Ward's, yield the most uniform cluster sizes and the best recovery of the true clusters. This result is expected since these two methods are biased toward recovering compact clusters of equal size. With average linkage, the lower-left cluster is too large; with the centroid method, the lower-right cluster is too large; and with two-stage density linkage, the top cluster is too large. The single linkage analysis resembles average linkage except for the large number of outliers resulting from the DOCK= option in the PROC TREE statement; the outliers are plotted as dots (missing values).
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.