The Desertification in Australia's Murray-Darling Basin
The Desertification in Australia's Murray-Darling Basin
The results from the two Multi-Criteria Evaluation analyses had concluded with my hypothesis. Human activity has a great impact on the desertification of Australia's Murray-Darling Basin. The environmental factors are Australia's annual averages, which do not vary much within a decade. The land use has changed significantly across Australia, resulting in the basin size reudction.
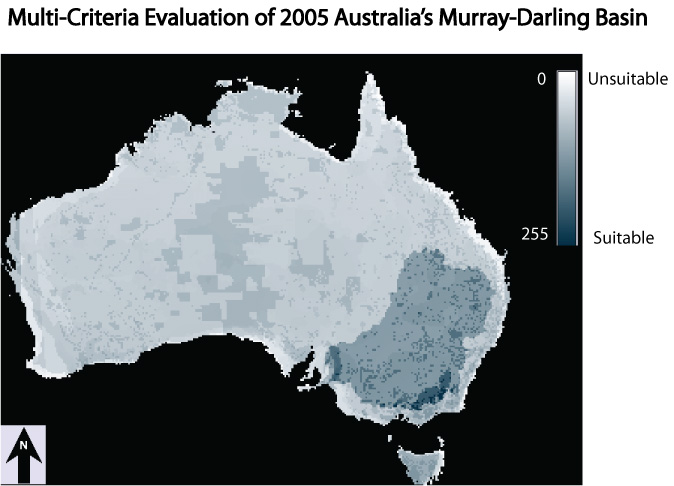
Between the two MCE analysis, the 1992 has a darker blue sprawled across the country. With 2005 land use data, there is a lot more light blue, and it is starting to affect the Murray-Darling Basin.
Pastrues and land for grazing have increased between 1992 data and 2005 data. Deforestation damages the soil. Soil will have difficulty absorbing the surface water, which cause a greater loss in water. Groundwater is able to retain moisture for a longer period of time.
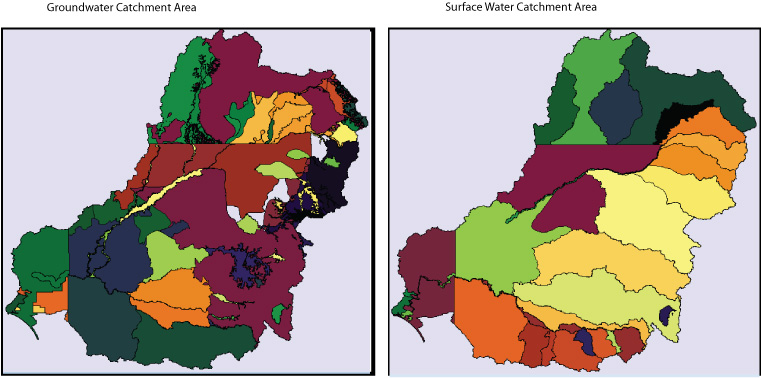
The groundwater on the left is divided up into several more catchment areas than the surface water on the right. By comparing the MCE of the Murray-Darling Basin, a lot of groundwater will be affected from the case of desertification.
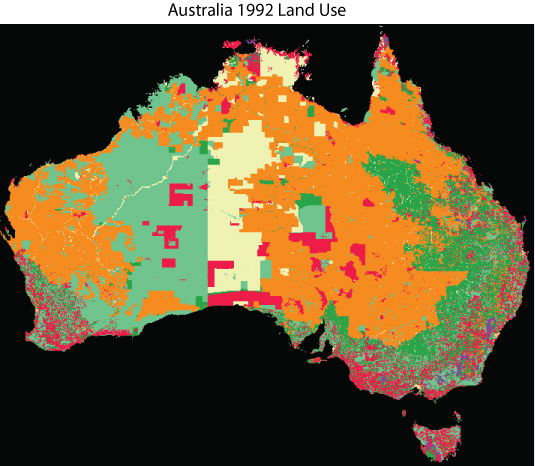
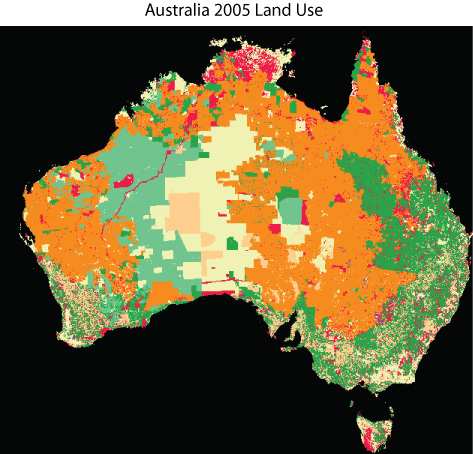
When looking at the two raster data, There are a lot more grazing (orange) and (dark green) in the 2005 data. In the 1992 data, more conservation land (pink) was present. Over the years it appears to have been eliminated, which could be an indication of the beginning of desertification, which may have caused the increase of grazing land.