Chapter Contents
Previous
Next
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Option |
Short Description |
| Estimation Methods | |
| G4=i | algorithm for computing STDERR |
| Optimization Techniques | |
| TECHNIQUE=name | minimization method |
| UPDATE=name | update technique |
| LINESEARCH=i | line-search method |
| FCONV=r | relative change function convergence criterion |
| GCONV=r | relative gradient convergence criterion |
| INSTEP=r | initial step length (SALPHA=, RADIUS=) |
| LSPRECISION=r | line-search precision |
| MAXFUNC=i | maximum number of function calls |
| MAXITER=i <n> | maximum number of iterations |
| Miscellaneous Options | |
| ASINGULAR=r | absolute singularity criterion for inversion of the information matrix |
| COVSING=r | singularity tolerance of the information matrix |
| MSINGULAR=r | relative M singularity criterion for inversion of the information matrix |
| SINGULAR=r | singularity criterion for inversion of the Hessian |
| VSINGULAR=r | relative V singularity criterion for inversion of the information matrix |
| Option |
Short Description |
| Options Used by All Techniques | |
| ABSCONV=r | absolute function convergence criterion |
| MAXFUNC=i | maximum number of function calls |
| MAXITER=i <n> | maximum number of iterations |
| MAXTIME=r | maximum CPU time |
| MINITER=i | minimum number of iterations |
| Options for Unconstrained and Linearly Constrained Techniques | |
| ABSFCONV=r <n> | absolute change function convergence criterion |
| ABSGCONV=r <n> | absolute gradient convergence criterion |
| ABSXCONV=r <n> | absolute change parameter convergence criterion |
| FCONV=r <n> | relative change function convergence criterion |
| FCONV2=r <n> | function convergence criterion |
| FDIGITS=r | precision in computation of the objective function |
| FSIZE=r | parameter for FCONV= and GCONV= |
| GCONV=r <n> | relative gradient convergence criterion |
| GCONV2=r <n> | relative gradient convergence criterion |
| XCONV=r <n> | relative change parameter convergence criterion |
| XSIZE=r | parameter for XCONV= |
| Options for Nonlinearly Constrained Techniques | |
| ABSGCONV=r <n> | maximum absolute gradient of Lagrange function criterion |
| FCONV2=r <n> | predicted objective function reduction criterion |
| GCONV=r <n> | normalized predicted objective function reduction criterion |
| Option |
Short Description |
| Options for the Approximate Covariance Matrix of Parameter Estimates | |
| CFACTOR=r | scalar factor for STDERR |
| NOHLF | use Hessian of the objective function for STDERR |
| Options for Additional Displayed Output | |
| PALL | display initial and final optimization values |
| PCRPJAC | display approximate Hessian matrix |
| PHESSIAN | display Hessian matrix |
| PHISTORY | display optimization history |
| PINIT | display initial values and derivatives (PALL) |
| PNLCJAC | display Jacobian matrix of nonlinear constraints (PALL) |
| display results of the optimization process | |
| Additional Options for Optimization Techniques | |
| DAMPSTEP< =r > | controls initial line-search step size |
| HESCAL=n | scaling version of Hessian or Jacobian |
| LCDEACT=r | Lagrange multiplier threshold of constraint |
| LCEPSILON=r | range for boundary and linear constraints |
| LCSINGULAR=r | QR decomposition linear dependence criterion |
| NOEIGNUM | suppress computation of matrices |
| RESTART=i | restart algorithm with a steepest descent direction |
| VERSION=1 | 2 | quasi-Newton optimization technique version |
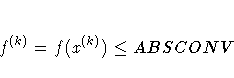
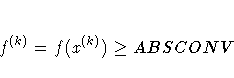
| TECH= | MAXFUNC default |
| LEVMAR, NEWRAP, NRRIDG, TRUREG | i=125 |
| DBLDOG, QUANEW | i=500 |
| CONGRA | i=1000 |
| TECH= | MAXITER default |
| LEVMAR, NEWRAP, NRRIDG, TRUREG | i=50 |
| DBLDOG, QUANEW | i=200 |
| CONGRA | i=400 |
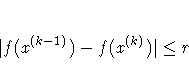

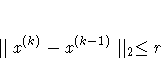
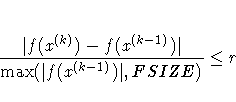
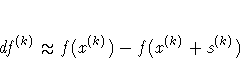
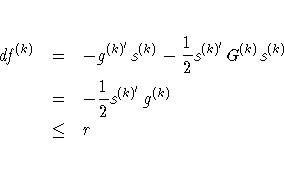
![{ [g^{(k)}]^' [G^{(k)}]^{-1} g^{(k)} \over
\max(| f(x^{(k)})|,FSIZE) } \leq r](images/caleq99.gif)
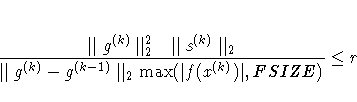
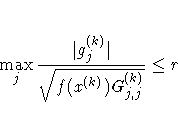
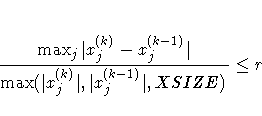
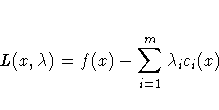

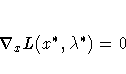
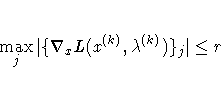

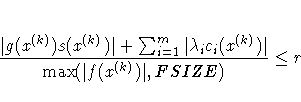
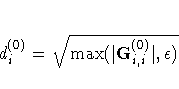
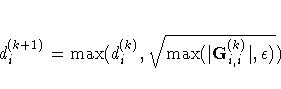
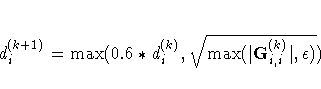
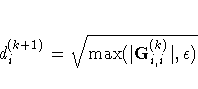
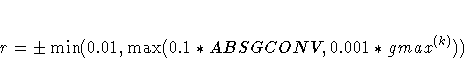
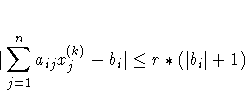
|
Chapter Contents |
Previous |
Next |
Top |
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.