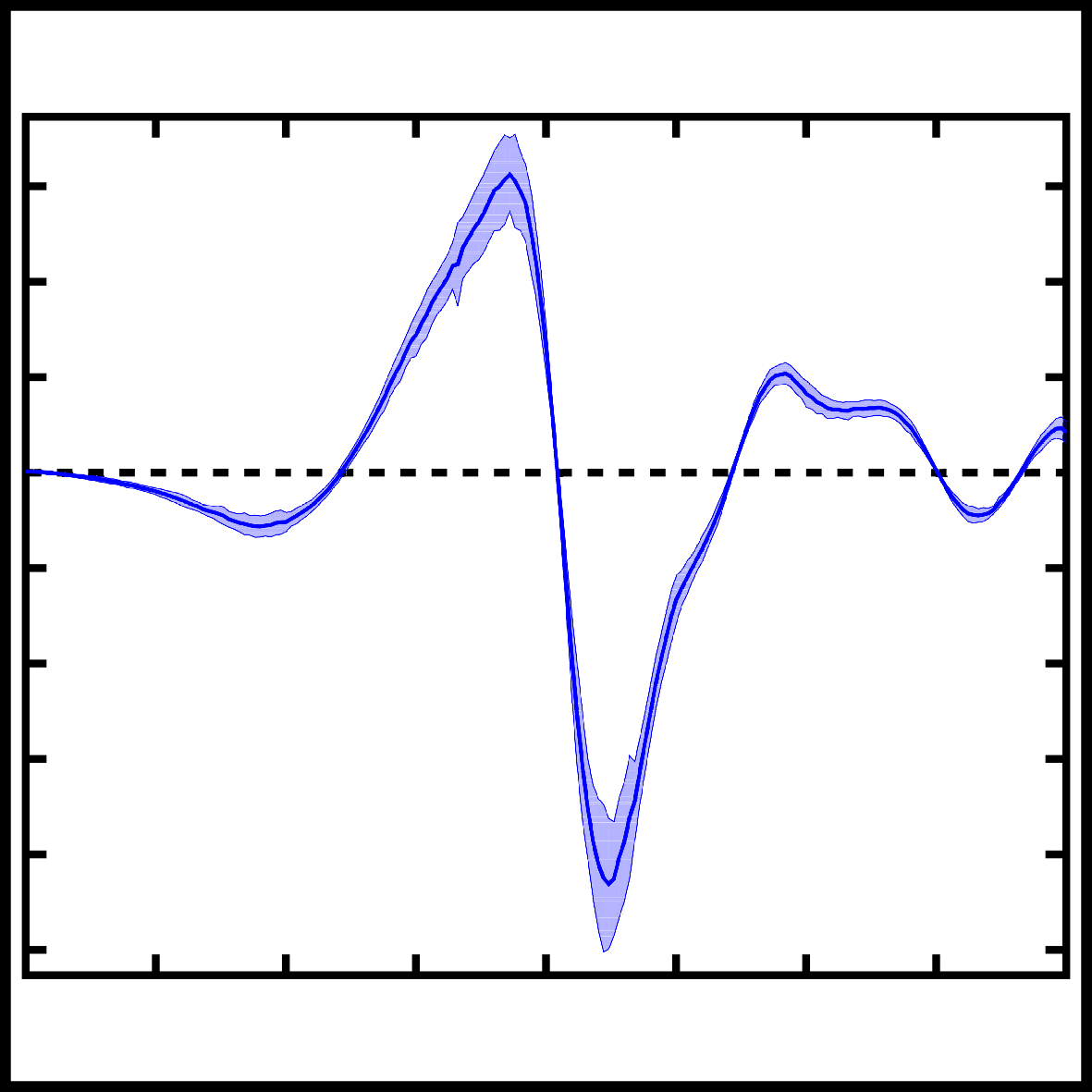
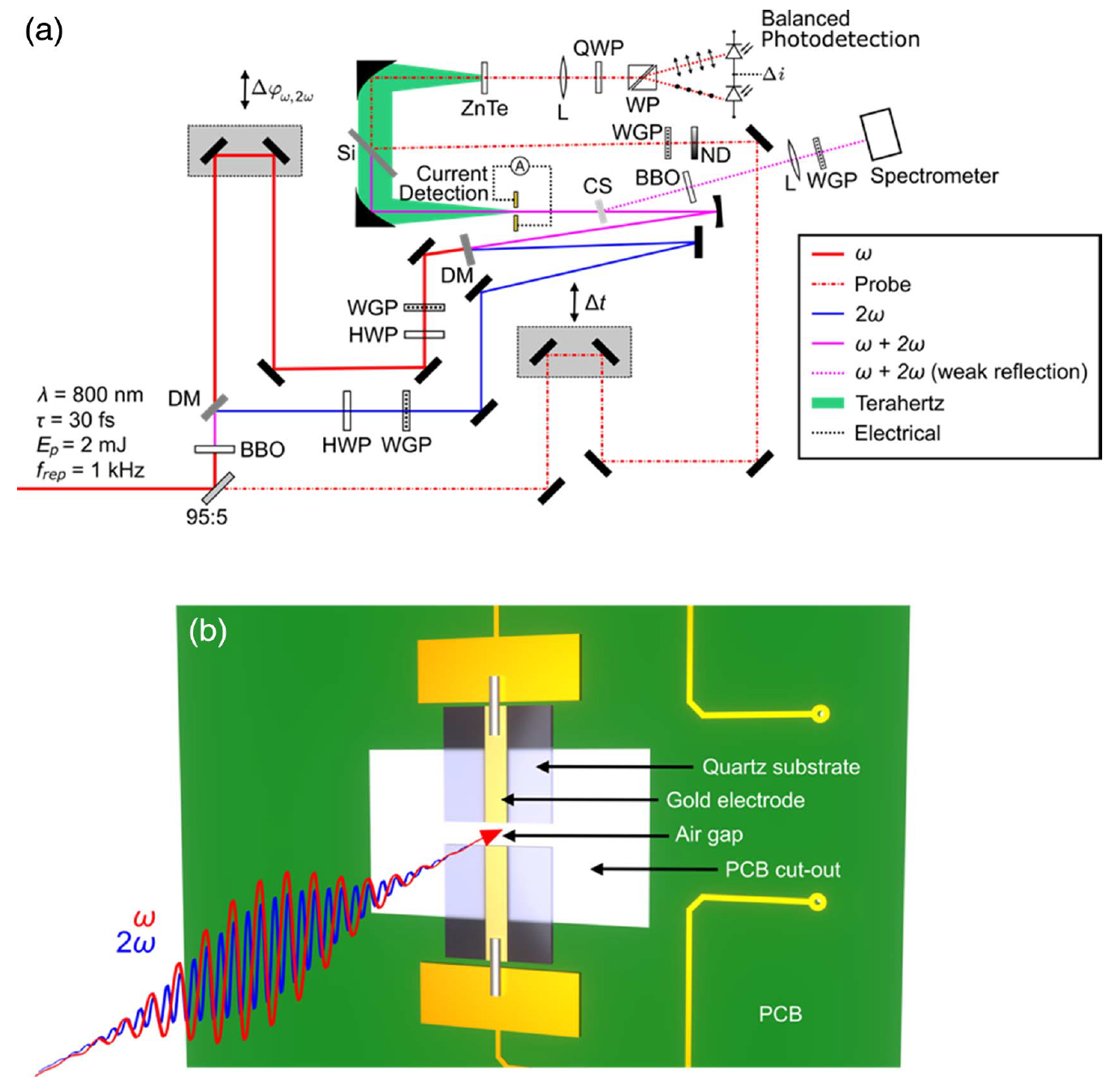
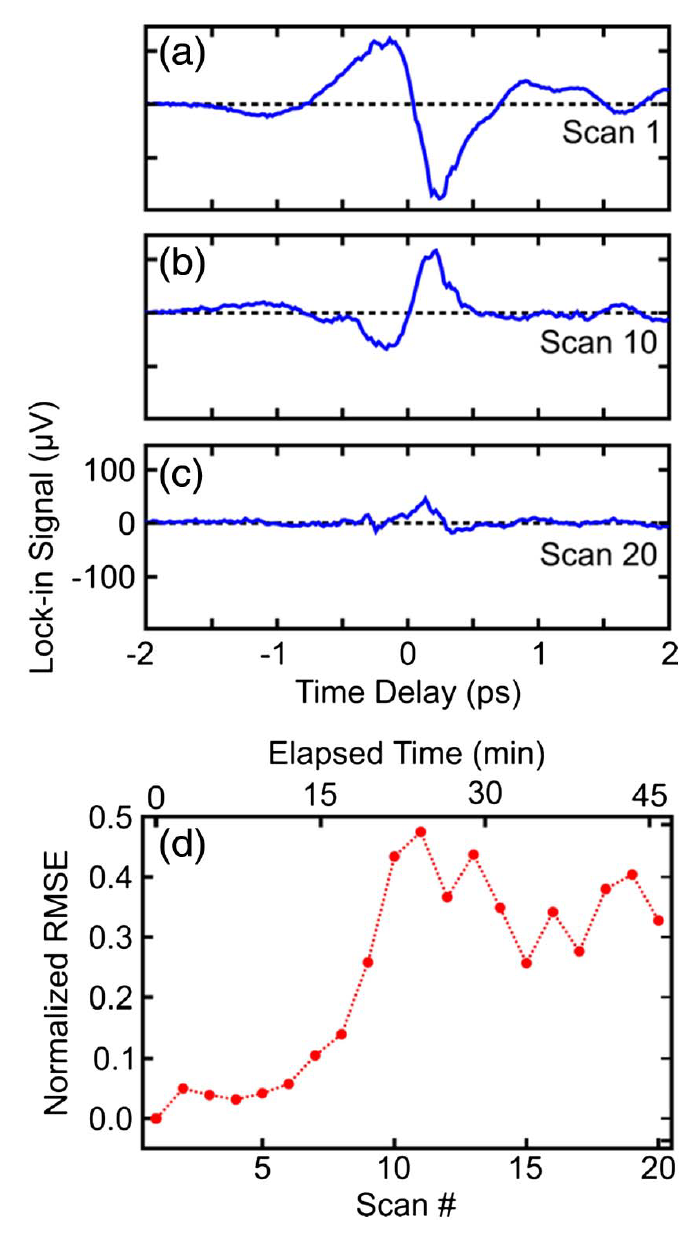
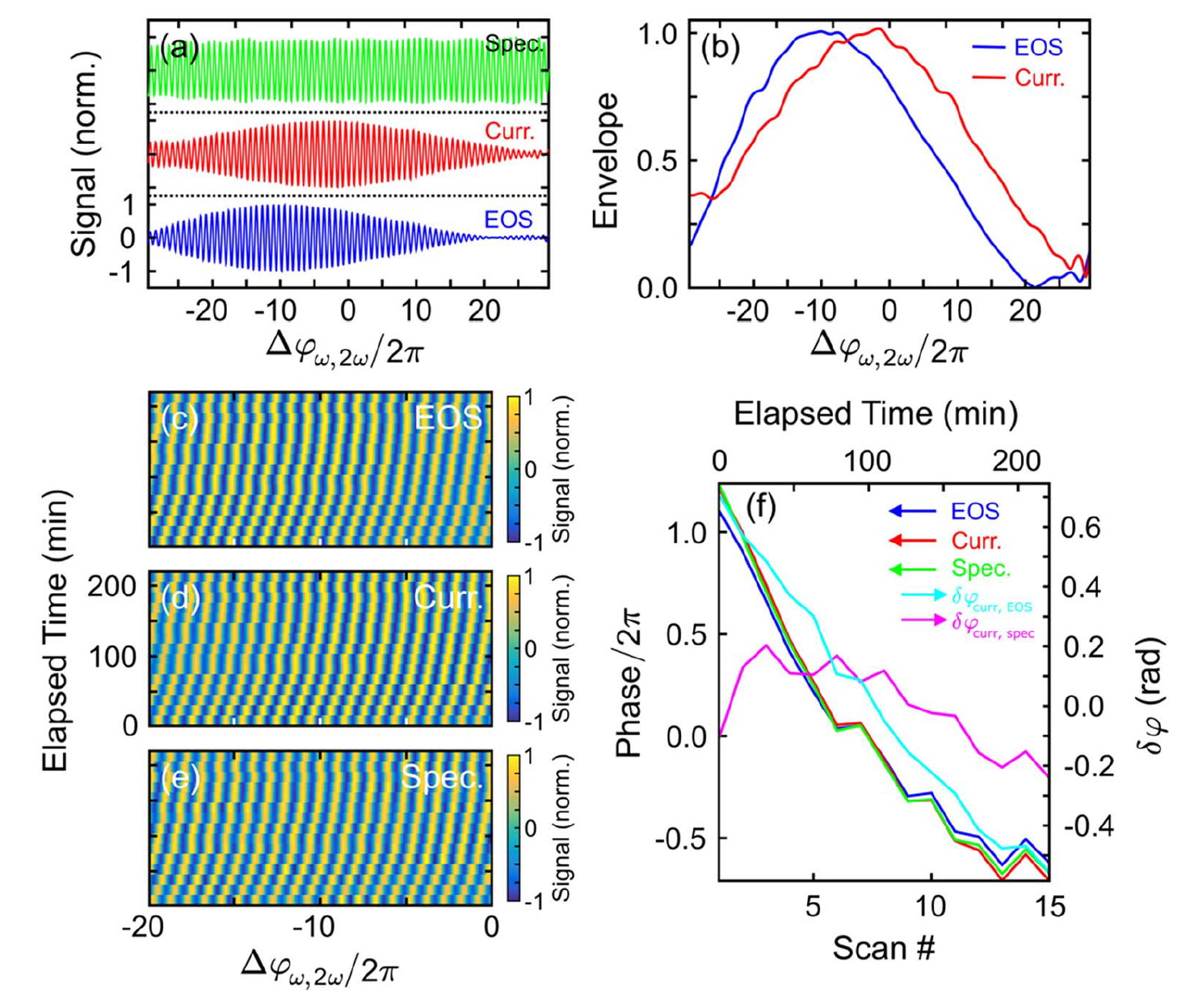
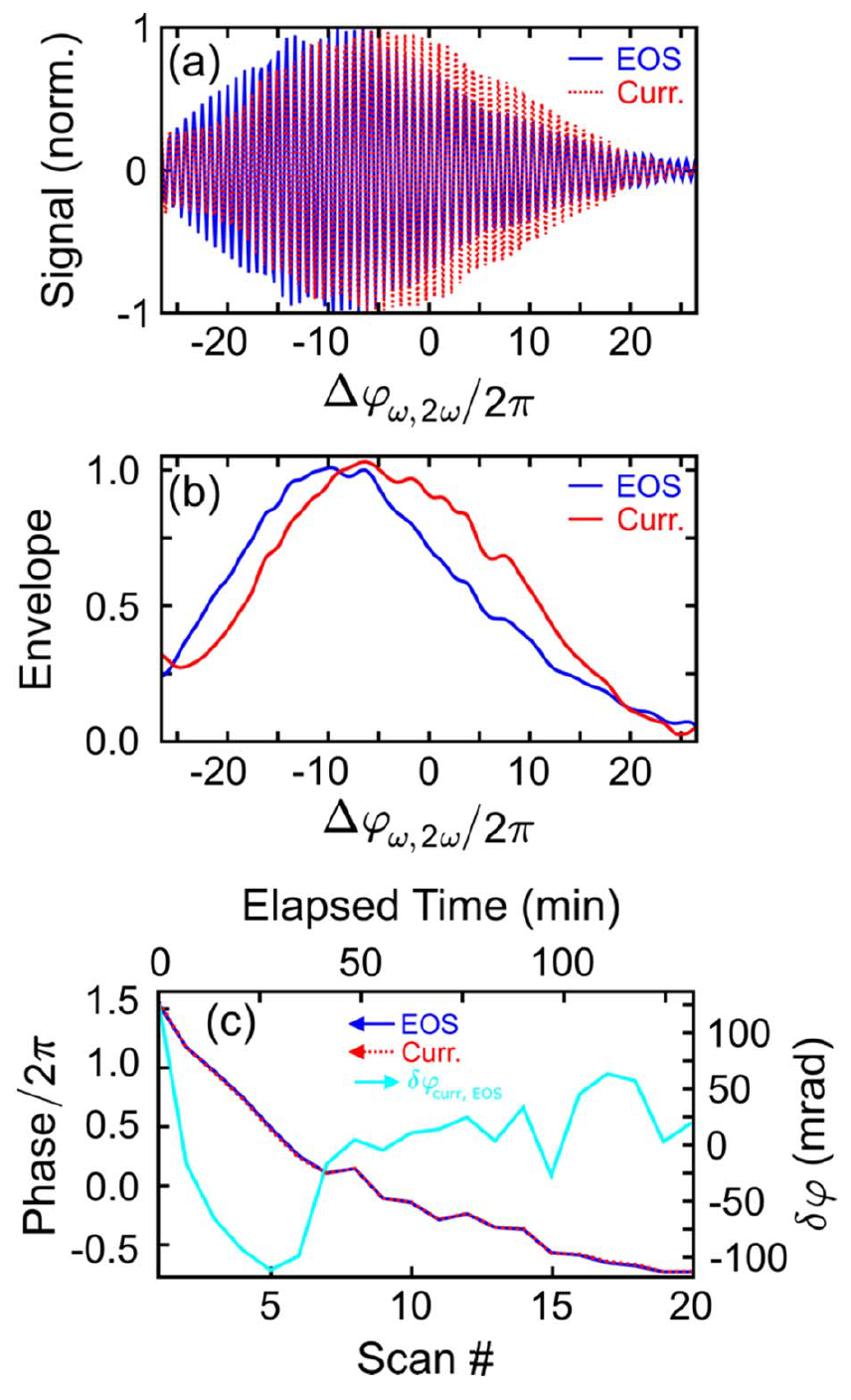
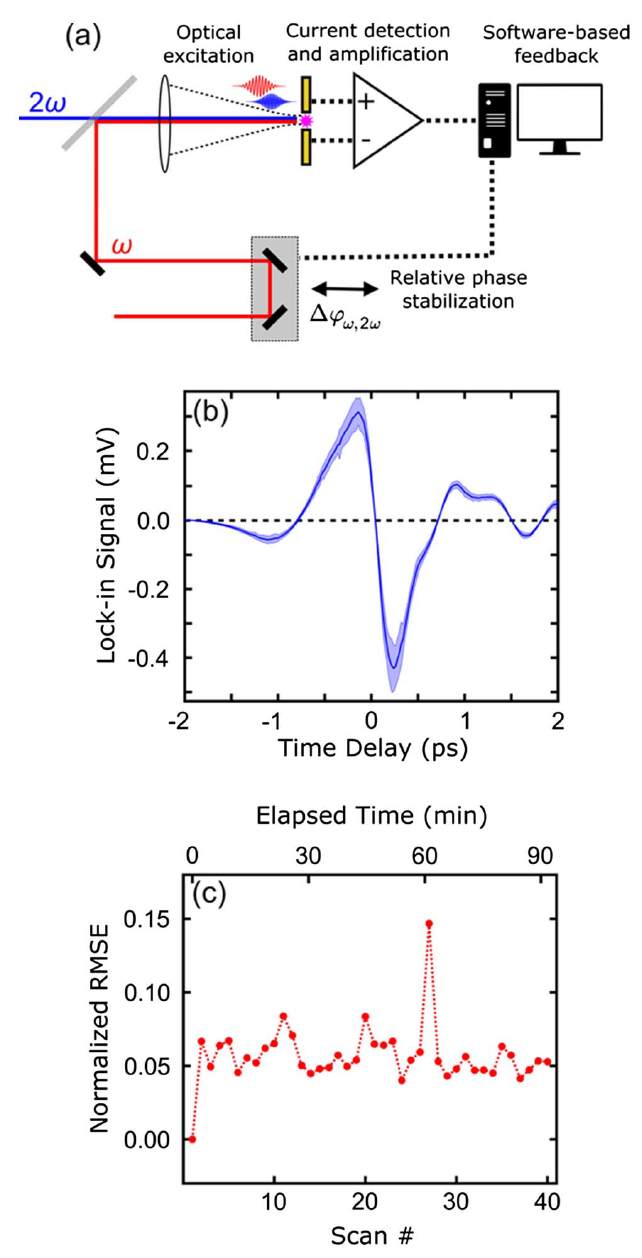
Abstract
Intense laser fields focused into ambient air can be used to generate high-bandwidth current densities in the form of plasma channels and filaments. Excitation with bichromatic fields enables us to adjust the amplitude and sign of these currents using the relative phase between the two light pulses. Two-color filamentation in gas targets provides a route to scaling the energy of terahertz pulses to microjoule levels by driving the plasma channel with a high-energy laser source. However, the structure of plasma channels is highly susceptible to drifts in both the relative phase and other laser parameters, making control over the waveform of the radiated terahertz fields delicate. We establish a clear link between the phase dependence of plasma currents and terahertz radiation by comparing in situ detection of current densities and far-field detection of terahertz electric fields. We show that the current measurement can be used as a feedback parameter for stabilizing the terahertz waveform. This approach provides a route to energetic terahertz pulses with exceptional waveform stability.