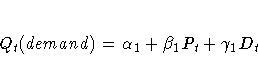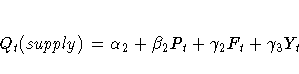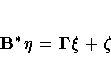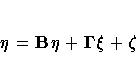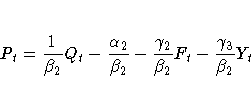Example 19.2: Simultaneous Equations with Intercept
The demand-and-supply food example of Kmenta (1971, pp. 565, 582)
is used to illustrate the use of PROC CALIS for the estimation
of intercepts and coefficients of simultaneous equations.
The model is specified by two simultaneous equations
containing two endogenous variables Q and P and three
exogenous variables D, F, and Y,
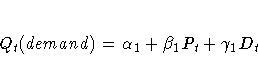
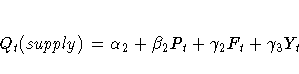
for t = 1, ... , 20.
The LINEQS statement requires that each endogenous variable appear
on the left-hand side of exactly one equation.
Instead of analyzing the system
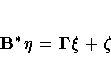
PROC CALIS analyzes the equivalent system
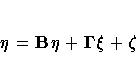
with B* = I- B. This requires that one of the preceding equations
be solved for Pt. Solving the second equation for Pt yields
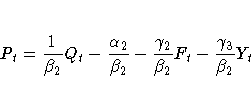
You can estimate the intercepts of a system of
simultaneous equations by applying PROC CALIS on the
uncorrected covariance (UCOV) matrix of the data set that is
augmented by an additional constant variable with the value 1.
In the following example, the uncorrected covariance matrix is
augmented by an additional variable INTERCEPT by using the AUGMENT
option. The PROC CALIS statement contains the options UCOV and AUG
to compute and analyze an augmented UCOV matrix from the input
data set FOOD.
data food;
Title 'Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582)';
Input Q P D F Y;
Label Q='Food Consumption per Head'
P='Ratio of Food Prices to General Price'
D='Disposable Income in Constant Prices'
F='Ratio of Preceding Years Prices'
Y='Time in Years 1922-1941';
datalines;
98.485 100.323 87.4 98.0 1
99.187 104.264 97.6 99.1 2
102.163 103.435 96.7 99.1 3
101.504 104.506 98.2 98.1 4
104.240 98.001 99.8 110.8 5
103.243 99.456 100.5 108.2 6
103.993 101.066 103.2 105.6 7
99.900 104.763 107.8 109.8 8
100.350 96.446 96.6 108.7 9
102.820 91.228 88.9 100.6 10
95.435 93.085 75.1 81.0 11
92.424 98.801 76.9 68.6 12
94.535 102.908 84.6 70.9 13
98.757 98.756 90.6 81.4 14
105.797 95.119 103.1 102.3 15
100.225 98.451 105.1 105.0 16
103.522 86.498 96.4 110.5 17
99.929 104.016 104.4 92.5 18
105.223 105.769 110.7 89.3 19
106.232 113.490 127.1 93.0 20
;
proc calis ucov aug data=food pshort;
Title2 'Compute ML Estimates With Intercept';
Lineqs
Q = alf1 Intercept + alf2 P + alf3 D + E1,
P = gam1 Intercept + gam2 Q + gam3 F + gam4 Y + E2;
Std
E1-E2 = eps1-eps2;
Cov
E1-E2 = eps3;
Bounds
eps1-eps2 >= 0. ;
run;
The following, essentially equivalent model definition uses
program code to reparameterize the model in terms of the original
equations; the output is displayed in Output 19.2.1.
proc calis data=food ucov aug pshort;
Lineqs
Q = alphal Intercept + beta1 P + gamma1 D + E1,
P = alpha2_b Intercept + gamma2_b F + gamma3_b Y + _b Q + E2;
Std
E1-E2 = eps1-eps2;
Cov
E1-E2 = eps3;
Parameters alpha2 (50.) beta2 gamma2 gamma3 (3*.25);
alpha2_b = -alpha2 / beta2;
gamma2_b = -gamma2 / beta2;
gamma3_b = -gamma3 / beta2;
_b = 1 / beta2;
Bounds
eps1-eps2 >= 0. ;
run;
Output 19.2.1: Food Example of Kmenta
| Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582) |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Covariance Structure Analysis: Pattern and Initial Values |
| LINEQS Model Statement |
| |
Matrix |
Rows |
Columns |
Matrix Type |
| Term 1 |
1 |
_SEL_ |
6 |
8 |
SELECTION |
|
| |
2 |
_BETA_ |
8 |
8 |
EQSBETA |
IMINUSINV |
| |
3 |
_GAMMA_ |
8 |
6 |
EQSGAMMA |
|
| |
4 |
_PHI_ |
6 |
6 |
SYMMETRIC |
|
| The 2 Endogenous Variables |
| Manifest |
Q P |
| Latent |
|
| The 6 Exogenous Variables |
| Manifest |
D F Y Intercept |
| Latent |
|
| Error |
E1 E2 |
|
| Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582) |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Covariance Structure Analysis: Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
| Parameter Estimates |
10 |
| Functions (Observations) |
21 |
| Lower Bounds |
2 |
| Upper Bounds |
0 |
| Optimization Start |
| Active Constraints |
0 |
Objective Function |
2.3500065042 |
| Max Abs Gradient Element |
203.9741437 |
Radius |
62167.829174 |
| Iteration |
|
Restarts |
Function
Calls |
Active
Constraints |
|
Objective
Function |
Objective
Function
Change |
Max Abs
Gradient
Element |
Lambda |
Ratio
Between
Actual
and
Predicted
Change |
| 1 |
|
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
1.19094 |
1.1591 |
3.9410 |
0 |
0.688 |
| 2 |
|
0 |
5 |
0 |
|
0.32678 |
0.8642 |
9.9864 |
0.00127 |
2.356 |
| 3 |
|
0 |
7 |
0 |
|
0.19108 |
0.1357 |
5.5100 |
0.00006 |
0.685 |
| 4 |
|
0 |
10 |
0 |
|
0.16682 |
0.0243 |
2.0513 |
0.00005 |
0.867 |
| 5 |
|
0 |
12 |
0 |
|
0.16288 |
0.00393 |
1.0570 |
0.00014 |
0.828 |
| 6 |
|
0 |
13 |
0 |
|
0.16132 |
0.00156 |
0.3643 |
0.00004 |
0.864 |
| 7 |
|
0 |
15 |
0 |
|
0.16077 |
0.000557 |
0.2176 |
0.00006 |
0.984 |
| 8 |
|
0 |
16 |
0 |
|
0.16052 |
0.000250 |
0.1819 |
0.00001 |
0.618 |
| 9 |
|
0 |
17 |
0 |
|
0.16032 |
0.000201 |
0.0662 |
0 |
0.971 |
| 10 |
|
0 |
18 |
0 |
|
0.16030 |
0.000011 |
0.0195 |
0 |
1.108 |
| 11 |
|
0 |
19 |
0 |
|
0.16030 |
6.116E-7 |
0.00763 |
0 |
1.389 |
| 12 |
|
0 |
20 |
0 |
|
0.16030 |
9.454E-8 |
0.00301 |
0 |
1.389 |
| 13 |
|
0 |
21 |
0 |
|
0.16030 |
1.461E-8 |
0.00118 |
0 |
1.388 |
| 14 |
|
0 |
22 |
0 |
|
0.16030 |
2.269E-9 |
0.000465 |
0 |
1.395 |
| 15 |
|
0 |
23 |
0 |
|
0.16030 |
3.59E-10 |
0.000182 |
0 |
1.427 |
| Optimization Results |
| Iterations |
15 |
Function Calls |
24 |
| Jacobian Calls |
16 |
Active Constraints |
0 |
| Objective Function |
0.1603035477 |
Max Abs Gradient Element |
0.0001820805 |
| Lambda |
0 |
Actual Over Pred Change |
1.4266532872 |
| Radius |
0.0010322573 |
|
|
| GCONV convergence criterion satisfied. |
|
| Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582) |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Covariance Structure Analysis: Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
| Fit Function |
0.1603 |
| Goodness of Fit Index (GFI) |
0.9530 |
| GFI Adjusted for Degrees of Freedom (AGFI) |
0.0120 |
| Root Mean Square Residual (RMR) |
2.0653 |
| Parsimonious GFI (Mulaik, 1989) |
0.0635 |
| Chi-Square |
3.0458 |
| Chi-Square DF |
1 |
| Pr > Chi-Square |
0.0809 |
| Independence Model Chi-Square |
534.27 |
| Independence Model Chi-Square DF |
15 |
| RMSEA Estimate |
0.3281 |
| RMSEA 90% Lower Confidence Limit |
. |
| RMSEA 90% Upper Confidence Limit |
0.7777 |
| ECVI Estimate |
1.8270 |
| ECVI 90% Lower Confidence Limit |
. |
| ECVI 90% Upper Confidence Limit |
3.3493 |
| Probability of Close Fit |
0.0882 |
| Bentler's Comparative Fit Index |
0.9961 |
| Normal Theory Reweighted LS Chi-Square |
2.8142 |
| Akaike's Information Criterion |
1.0458 |
| Bozdogan's (1987) CAIC |
-0.9500 |
| Schwarz's Bayesian Criterion |
0.0500 |
| McDonald's (1989) Centrality |
0.9501 |
| Bentler & Bonett's (1980) Non-normed Index |
0.9409 |
| Bentler & Bonett's (1980) NFI |
0.9943 |
| James, Mulaik, & Brett (1982) Parsimonious NFI |
0.0663 |
| Z-Test of Wilson & Hilferty (1931) |
1.4250 |
| Bollen (1986) Normed Index Rho1 |
0.9145 |
| Bollen (1988) Non-normed Index Delta2 |
0.9962 |
| Hoelter's (1983) Critical N |
25 |
|
| Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582) |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Covariance Structure Analysis: Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
| Q |
= |
-0.2295 |
* |
P |
+ |
0.3100 |
* |
D |
+ |
93.6193 |
* |
Intercept |
+ |
1.0000 |
|
E1 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
beta1 |
|
|
|
gamma1 |
|
|
|
alphal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| P |
= |
4.2140 |
* |
Q |
+ |
-0.9305 |
* |
F |
+ |
-1.5579 |
* |
Y |
+ |
-218.9 |
* |
Intercept |
+ |
1.0000 |
|
E2 |
| |
|
|
|
_b |
|
|
|
gamma2_b |
|
|
|
gamma3_b |
|
|
|
alpha2_b |
|
|
|
|
|
| Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582) |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Covariance Structure Analysis: Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
| Variances of Exogenous Variables |
| Variable |
Parameter |
Estimate |
| D |
|
10154 |
| F |
|
9989 |
| Y |
|
151.05263 |
| Intercept |
|
1.05263 |
| E1 |
eps1 |
3.51274 |
| E2 |
eps2 |
105.06746 |
| Covariances Among Exogenous Variables |
| Var1 |
Var2 |
Parameter |
Estimate |
| D |
F |
|
9994 |
| D |
Y |
|
1101 |
| F |
Y |
|
1046 |
| D |
Intercept |
|
102.66842 |
| F |
Intercept |
|
101.71053 |
| Y |
Intercept |
|
11.05263 |
| E1 |
E2 |
eps3 |
-18.87270 |
|
| Food example of KMENTA(1971, p.565 & 582) |
| The CALIS Procedure |
| Covariance Structure Analysis: Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
| Q |
= |
-0.2278 |
* |
P |
+ |
0.3016 |
* |
D |
+ |
0.9272 |
* |
Intercept |
+ |
0.0181 |
|
E1 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
beta1 |
|
|
|
gamma1 |
|
|
|
alphal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| P |
= |
4.2467 |
* |
Q |
+ |
-0.9048 |
* |
F |
+ |
-0.1863 |
* |
Y |
+ |
-2.1849 |
* |
Intercept |
+ |
0.0997 |
|
E2 |
| |
|
|
|
_b |
|
|
|
gamma2_b |
|
|
|
gamma3_b |
|
|
|
alpha2_b |
|
|
|
|
| Squared Multiple Correlations |
| |
Variable |
Error Variance |
Total Variance |
R-Square |
| 1 |
Q |
3.51274 |
10730 |
0.9997 |
| 2 |
P |
105.06746 |
10565 |
0.9901 |
| Correlations Among Exogenous Variables |
| Var1 |
Var2 |
Parameter |
Estimate |
| D |
F |
|
0.99237 |
| D |
Y |
|
0.88903 |
| F |
Y |
|
0.85184 |
| D |
Intercept |
|
0.99308 |
| F |
Intercept |
|
0.99188 |
| Y |
Intercept |
|
0.87652 |
| E1 |
E2 |
eps3 |
-0.98237 |
| Additional PARMS and Dependent Parameters |
| The Number of Dependent Parameters is 4 |
| Parameter |
Estimate |
Standard
Error |
t Value |
| alpha2 |
51.94453 |
. |
. |
| beta2 |
0.23731 |
. |
. |
| gamma2 |
0.22082 |
. |
. |
| gamma3 |
0.36971 |
. |
. |
| _b |
4.21397 |
. |
. |
| gamma2_b |
-0.93053 |
. |
. |
| gamma3_b |
-1.55794 |
. |
. |
| alpha2_b |
-218.89288 |
. |
. |
|
You can obtain almost equivalent results by applying
the SAS/ETS procedure SYSLIN on this problem.
Copyright © 1999 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.